Plant nuclear envelope as a hub connecting genome organization with regulation of gene expression
- PMID: 36794966
- PMCID: PMC9980628
- DOI: 10.1080/19491034.2023.2178201
Plant nuclear envelope as a hub connecting genome organization with regulation of gene expression
Abstract
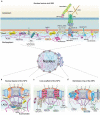
Eukaryotic cells organize their genome within the nucleus with a double-layered membrane structure termed the nuclear envelope (NE) as the physical barrier. The NE not only shields the nuclear genome but also spatially separates transcription from translation. Proteins of the NE including nucleoskeleton proteins, inner nuclear membrane proteins, and nuclear pore complexes have been implicated in interacting with underlying genome and chromatin regulators to establish a higher-order chromatin architecture. Here, I summarize recent advances in the knowledge of NE proteins that are involved in chromatin organization, gene regulation, and coordination of transcription and mRNA export. These studies support an emerging view of plant NE as a central hub that contributes to chromatin organization and gene expression in response to various cellular and environmental cues.
Keywords: Nuclear envelope; gene expression; genome organization; nuclear lamina; nuclear membrane; nuclear pore complex; plants.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear pore biogenesis into an intact nuclear envelope.Chromosoma. 2010 Oct;119(5):469-77. doi: 10.1007/s00412-010-0289-2. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Chromosoma. 2010. PMID: 20721671 Review.
-
Till disassembly do us part: a happy marriage of nuclear envelope and chromatin.J Biochem. 2008 Feb;143(2):155-61. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvm219. Epub 2007 Nov 12. J Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17999983 Review.
-
The plant nuclear envelope and regulation of gene expression.J Exp Bot. 2015 Mar;66(6):1673-85. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv023. Epub 2015 Feb 13. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25680795 Review.
-
Regulation and coordination of nuclear envelope and nuclear pore complex assembly.Nucleus. 2013 Mar-Apr;4(2):105-14. doi: 10.4161/nucl.23796. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Nucleus. 2013. PMID: 23412657 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamic Nature of the Nuclear Envelope.Curr Biol. 2018 Apr 23;28(8):R487-R497. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.073. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29689232 Review.
Cited by
-
CRWN nuclear lamina components maintain the H3K27me3 landscape and promote successful reproduction in Arabidopsis.New Phytol. 2024 Jul;243(1):213-228. doi: 10.1111/nph.19791. Epub 2024 May 7. New Phytol. 2024. PMID: 38715414 Free PMC article.
-
Proxiome assembly of the plant nuclear pore reveals an essential hub for gene expression regulation.Nat Plants. 2024 Jun;10(6):1005-1017. doi: 10.1038/s41477-024-01698-9. Epub 2024 May 21. Nat Plants. 2024. PMID: 38773271
-
Physical model of the nuclear membrane permeability mechanism.Biophys Rev. 2023 Oct 4;15(5):1195-1207. doi: 10.1007/s12551-023-01136-8. eCollection 2023 Oct. Biophys Rev. 2023. PMID: 37974978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidics to Follow Spatiotemporal Dynamics at the Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Interface During Plant Root Growth.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2873:223-245. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4228-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39576605
-
Nuclear lamina component KAKU4 regulates chromatin states and transcriptional regulation in the Arabidopsis genome.BMC Biol. 2024 Apr 12;22(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01882-5. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 38609974 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
