Comparison of CalliSpheres® microspheres drug-eluting beads and conventional transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 36794998
- PMCID: PMC10039469
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2023-0001
Comparison of CalliSpheres® microspheres drug-eluting beads and conventional transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: This trial aimed to compare the outcomes of drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization (DEB-TACE) with CalliSpheres® microspheres (CSM) and conventional transarterial chemoembolization cTACE in the treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Patients and methods: A total of 90 patients were divided into DEB-TACE group (n = 45) and cTACE group (n = 45). The treatment response, overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and the safety were compared between the two groups.
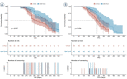
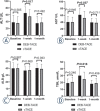
Results: The objective response rate (ORR) in the DEB-TACE group was significantly higher than that in cTACE group at 1, 3, and 6 months of follow-up (P = 0.031, P = 0.003, P = 0.002). The complete response (CR) in DEB-TACE group was significantly higher than that in cTACE group at 3 months (P = 0.036). Survival analysis revealed that, DEB-TACE group had better survival benefits than cTACE group (median OS: 534 days vs. 367 days, P = 0.027; median PFS: 352 days vs. 278 days P = 0.004). The degree of liver function injury was more serious in DEB-TACE group at 1 week, but was similar between the two groups at 1 month. DEB-TACE with CSM caused a high incidence of fever and a severe abdominal pain (P = 0.031, P = 0.037).
Conclusions: DEB-TACE with CSM showed better treatment response and survival benefits than cTACE group. Although a transient more severe liver damage, high incidence of fever and a severe abdominal pain occurred in the DEB-TACE group, it could be resolved through symptomatic treatment.
Keywords: CalliSpheres® microspheres; DEB-TACE; cTACE; hepatocellular carcinoma; tumor response.
© 2023 Zhongxing Shi, Dongqing Wang, Tanrong Kang, Ru Yi, Liming Cui, Huijie Jiang, published by Sciendo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CalliSpheres drug-eluting beads versus lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a short-term efficacy and safety study.World J Surg Oncol. 2018 Mar 27;16(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1368-8. World J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29587773 Free PMC article.
-
Callispheres® drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization might be an efficient and safety down-staging therapy in unresectable liver cancer patients.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Aug 9;20(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02717-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35941634 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of treatment response, survival and safety between drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization with CalliSpheres® microspheres versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization in treating hepatocellular carcinoma.J BUON. 2019 May-Jun;24(3):1150-1166. J BUON. 2019. PMID: 31424674
-
Treatment Response, Survival, and Safety of Transarterial Chemoembolization With CalliSpheres® Microspheres Versus Conventional Transarterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 16;11:576232. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.576232. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33796448 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial strategies for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 19;15(2):e0227475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227475. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32074102 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Locoregional Therapies for Hepatobiliary Tumors: Contemporary Strategies and Novel Applications.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 25;16(7):1271. doi: 10.3390/cancers16071271. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38610949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Simple Prognostic Scoring System for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with DEB-TACE.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jul 10;11:1403-1414. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S458657. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39005968 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and prediction of the efficacy and influencing factors of camrelizumab combined with TACE and sorafenib in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;149(13):12479-12487. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05050-0. Epub 2023 Jul 14. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37450029 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of D-TACE followed by D-RFA for unresectable large hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 28;15:1530951. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1530951. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40792272 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal side effects in hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving transarterial chemoembolization: a meta-analysis of 81 studies and 9495 patients.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025 Feb 7;17:17588359251316663. doi: 10.1177/17588359251316663. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39926261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C, Qiu H, Yao Y, Zhang Z, Ma C, Ma Y. Comprehensive predictive factors for CalliSpheres® microspheres (CSM) drug-eluting bead-transarterial chemoembolization and conventional transarterial chemoembolization on treatment response and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2021;45:101460. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2020.05.008. et al. doi. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
