Selective Hydrolysis of Nonactivated Aryl Esters at pH 7 through Cooperative Catalysis
- PMID: 36795622
- PMCID: PMC10183976
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c02570
Selective Hydrolysis of Nonactivated Aryl Esters at pH 7 through Cooperative Catalysis
Abstract
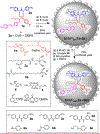
Most reported artificial esterases only hydrolyze highly activated substrates. We here report synthetic catalysts that hydrolyze nonactivated aryl esters at pH 7, via cooperative action of a thiourea group that mimics the oxyanion hole of a serine protease and a nearby nucleophilic/basic pyridyl group. The molecularly imprinted active site distinguishes subtle structural changes in the substrate, including elongation of the acyl chain by two carbons or shift of a remote methyl group by one carbon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Artificial Esterase for Cooperative Catalysis of Ester Hydrolysis at pH 7.Mater Today Chem. 2023 Jun;30:101576. doi: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2023.101576. Epub 2023 May 18. Mater Today Chem. 2023. PMID: 37997572 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinted Polymeric Nanoparticles as Artificial Enzymes for Ester Hydrolysis at Room Temperature and pH 7.Chem Catal. 2022 Aug 18;2(8):2049-2065. doi: 10.1016/j.checat.2022.06.007. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Chem Catal. 2022. PMID: 38098612 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Hydrolysis of Aryl Esters under Acidic and Neutral Conditions by a Synthetic Aspartic Protease Mimic.ACS Catal. 2021 Apr 2;11(7):3938-3942. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.1c00371. Epub 2021 Mar 16. ACS Catal. 2021. PMID: 34422449 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic anhydrase mimics with rationally designed active sites for fine-tuned catalytic activity and selectivity in ester hydrolysis.Catal Sci Technol. 2023 Aug 22;13(19):5702-5709. doi: 10.1039/d3cy00704a. eCollection 2023 Oct 2. Catal Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 38013842 Free PMC article.
-
Blood cholinesterases as human biomarkers of organophosphorus pesticide exposure.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000;163:29-111. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-6429-1_2. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000. PMID: 10771584 Review.
References
-
- Dodso G.; Wlodawe A. Catalytic Triads and Their Relatives. Trends Biochem. Sci 1998, 23, 347–352. - PubMed
-
- Corey DR; Craik CS An Investigation into the Minimum Requirements for Peptide Hydrolysis by Mutation of the Catalytic Triad of Trypsin. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1992, 114, 1784–1790.
-
- Craik CS; Roczniak S; Largman C; Rutter WJ The Catalytic Role of the Active Site Aspartic Acid in Serine Proteases. Science 1987, 237, 909–913. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald MJ; Lavis LD; Hilvert D; Gellman SH Evaluation of the Ser-His Dipeptide, a Putative Catalyst of Amide and Ester Hydrolysis. Org. Lett 2016, 18, 3518–3521. - PubMed
-
- Nothling MD; Ganesan A; Condic-Jurkic K; Pressly E; Davalos A; Gotrik MR; Xiao Z; Khoshdel E; Hawker CJ; O’Mara ML; Coote ML; Connal LA Simple Design of an Enzyme-Inspired Supported Catalyst Based on a Catalytic Triad. Chem 2017, 2, 732–745.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

