Precision Neoantigen Discovery Using Large-Scale Immunopeptidomes and Composite Modeling of MHC Peptide Presentation
- PMID: 36796642
- PMCID: PMC10114598
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100506
Precision Neoantigen Discovery Using Large-Scale Immunopeptidomes and Composite Modeling of MHC Peptide Presentation
Abstract
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-bound peptides that originate from tumor-specific genetic alterations, known as neoantigens, are an important class of anticancer therapeutic targets. Accurately predicting peptide presentation by MHC complexes is a key aspect of discovering therapeutically relevant neoantigens. Technological improvements in mass spectrometry-based immunopeptidomics and advanced modeling techniques have vastly improved MHC presentation prediction over the past 2 decades. However, improvement in the accuracy of prediction algorithms is needed for clinical applications like the development of personalized cancer vaccines, the discovery of biomarkers for response to immunotherapies, and the quantification of autoimmune risk in gene therapies. Toward this end, we generated allele-specific immunopeptidomics data using 25 monoallelic cell lines and created Systematic Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Epitope Ranking Pan Algorithm (SHERPA), a pan-allelic MHC-peptide algorithm for predicting MHC-peptide binding and presentation. In contrast to previously published large-scale monoallelic data, we used an HLA-null K562 parental cell line and a stable transfection of HLA allele to better emulate native presentation. Our dataset includes five previously unprofiled alleles that expand MHC diversity in the training data and extend allelic coverage in underprofiled populations. To improve generalizability, SHERPA systematically integrates 128 monoallelic and 384 multiallelic samples with publicly available immunoproteomics data and binding assay data. Using this dataset, we developed two features that empirically estimate the propensities of genes and specific regions within gene bodies to engender immunopeptides to represent antigen processing. Using a composite model constructed with gradient boosting decision trees, multiallelic deconvolution, and 2.15 million peptides encompassing 167 alleles, we achieved a 1.44-fold improvement of positive predictive value compared with existing tools when evaluated on independent monoallelic datasets and a 1.17-fold improvement when evaluating on tumor samples. With a high degree of accuracy, SHERPA has the potential to enable precision neoantigen discovery for future clinical applications.
Keywords: MHC; cancer; cancer vaccines; immunology; immunopeptidomics; machine learning; major histocompatibility complex; neoantigen prediction; neoantigens; next-generation sequencing.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest R. M. P., D. M., Steven Dea, C. A., S. V. Z., N. A. P., J. H., G. B., Sejal Desai, R. M., J. W., R. C., and S. M. B. are full-time employees of Personalis. M. P. S. cofounded Personalis. Personalis Inc provided the funding for this project.
Figures
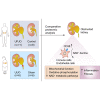


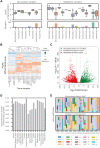
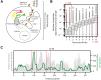

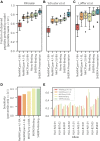
Corrected and republished from
-
Withdrawal of 'Precision Neoantigen Discovery Using Large-scale Immunopeptidomes and Composite Modeling of MHC Peptide Presentation'.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023 Apr;22(4):100511. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100511. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023. Corrected and republished in: Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023 Apr;22(4):100506. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100506. PMID: 37019059 Free PMC article. Corrected and republished. No abstract available.
References
-
- Yadav M., Jhunjhunwala S., Phung Q.T., Lupardus P., Tanguay J., Bumbaca S., et al. Predicting immunogenic tumour mutations by combining mass spectrometry and exome sequencing. Nature. 2014;515:572–576. - PubMed
-
- Schumacher T.N., Schreiber R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science. 2015;348:69–74. - PubMed
-
- Sette A., Vitiello A., Reherman B., Fowler P., Nayersina R., Kast W.M., et al. The relationship between class I binding affinity and immunogenicity of potential cytotoxic T cell epitopes. J. Immunol. 1994;153:5586–5592. - PubMed
-
- Hunt D.F., Henderson R.A., Shabanowitz J., Sakaguchi K., Michel H., Sevilir N., et al. Characterization of peptides bound to the class I MHC molecule HLA-A2.1 by mass spectrometry. Science. 1992;255:1261–1263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

