Novel anatomical guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection in the mentalis muscle: a review
- PMID: 36796830
- PMCID: PMC10520866
- DOI: 10.5115/acb.22.266
Novel anatomical guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection in the mentalis muscle: a review
Abstract
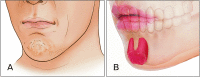
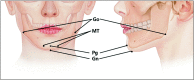
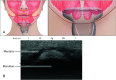
The mentalis muscle is a paired muscle originating from the alveolar bone of the mandible. This muscle is the main target muscle for botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) injection therapy, which aims to treat cobblestone chin caused by mentalis hyperactivity. However, a lack of knowledge on the anatomy of the mentalis muscle and the properties of BoNT can lead to side effects, such as mouth closure insufficiency and smile asymmetry due to ptosis of the lower lip after BoNT injection procedures. Therefore, we have reviewed the anatomical properties associated with BoNT injection into the mentalis muscle. An up-to-date understanding of the localization of the BoNT injection point according to mandibular anatomy leads to better injection localization into the mentalis muscle. Optimal injection sites have been provided for the mentalis muscle and a proper injection technique has been described. We have suggested optimal injection sites based on the external anatomical landmarks of the mandible. The aim of these guidelines is to maximize the effects of BoNT therapy by minimizing the deleterious effects, which can be very useful in clinical settings.
Keywords: Botulinum neurotoxin; Cobblestone chin; Facial wrinkle; Injection point; Mentalis muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have all considered the conflict of interest statement included in “Author Guidelines”. To the best of our knowledge, no aspect of the authors’ current personal or professional life might significantly affect the views presented on this manuscript. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
