Couple-based lifestyle intervention to prevent type 2 diabetes: protocol for a randomised pilot trial
- PMID: 36797025
- PMCID: PMC9936286
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068623
Couple-based lifestyle intervention to prevent type 2 diabetes: protocol for a randomised pilot trial
Abstract
Introduction: Type 2 diabetes is prevalent among US adults. Lifestyle interventions that modify health behaviours prevent or delay progression to diabetes among individuals at high risk. Despite the well-documented influence of individuals' social context on their health, evidence-based type 2 diabetes prevention interventions do not systematically incorporate participants' romantic partners. Involving partners of individuals at high risk for type 2 diabetes in primary prevention may improve engagement and outcomes of programmes. The randomised pilot trial protocol described in this manuscript will evaluate a couple-based lifestyle intervention to prevent type 2 diabetes. The objective of the trial is to describe the feasibility of the couple-based intervention and the study protocol to guide planning of a definitive randomised clinical trial (RCT).
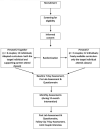
Methods and analysis: We used community-based participatory research principles to adapt an individual diabetes prevention curriculum for delivery to couples. This parallel two-arm pilot study will include 12 romantic couples in which at least one partner (ie, 'target individual') is at risk for type 2 diabetes. Couples will be randomised to either the 2021 version of the CDC's PreventT2 curriculum designed for delivery to individuals (six couples), or PreventT2 Together, the adapted couple-based curriculum (six couples). Participants and interventionists will be unblinded, but research nurses collecting data will be blinded to treatment allocation. Feasibility of the couple-based intervention and the study protocol will be assessed using both quantitative and qualitative measures.
Ethics and dissemination: This study has been approved by the University of Utah IRB (#143079). Findings will be shared with researchers through publications and presentations. We will collaborate with community partners to determine the optimal strategy for communicating findings to community members. Results will inform a subsequent definitive RCT.
Trial registration number: NCT05695170.
Keywords: DIABETES & ENDOCRINOLOGY; NUTRITION & DIETETICS; PREVENTIVE MEDICINE; PUBLIC HEALTH.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at http://www.icmje.org/disclosure-of-interest/ and declare: DG’s institution has received consulting fees from Medtronic, Abbott, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly and Optum and DG was also a past president of Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists: Minnesota state chapter; KH is the programme coordinator for the Special Diabetes Program for Indians, has received travel and conference funds through the Urban Indian Center of Salt Lake, and is the planning committee co-chair for the Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists Utah Annual Diabetes Update Conference; KB is a Representative-at-Large on the Association for Behavioral and Cognitive Therapies Board of Directors and was a Member-at-Large on the Society for a Science of Clinical Psychology Board of Directors; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- National Center for Health Statistics . Leading causes of death. Cent Dis Control Prev 2019. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/leading-causes-of-death.htm
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National diabetes statistics report. US Dep Health Hum Serv 2022. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical