Circadian Disruption in Night Shift Work and Its Association with Chronic Pulmonary Diseases
- PMID: 36797209
- PMCID: PMC12341038
- DOI: 10.1002/adbi.202200292
Circadian Disruption in Night Shift Work and Its Association with Chronic Pulmonary Diseases
Abstract
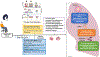
Globalization and the expansion of essential services over continuous 24 h cycles have necessitated the adaptation of the human workforce to shift-based schedules. Night shift work (NSW) causes a state of desynchrony between the internal circadian machinery and external environmental cues, which can impact inflammatory and metabolic pathways. The discovery of clock genes in the lung has shed light on potential mechanisms of circadian misalignment in chronic pulmonary disease. Here, the current knowledge of circadian clock disruption caused by NSW and its impact on lung inflammation and associated pathophysiology in chronic lung diseases, such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary fibrosis, and COVID-19, is reviewed. Furthermore, the limitations of the current understanding of circadian disruption and potential future chronotherapeutic advances are discussed.
Keywords: asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; circadian disruption; clock genes; night shift work; pulmonary fibrosis.
© 2023 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
How Shift Work Affects Our Gut Microbiota: Impact on Gastrointestinal Diseases.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 May 27;61(6):995. doi: 10.3390/medicina61060995. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40572683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of shift-work light conditions on tissue-specific circadian rhythms of canonical clock genes: insights from a mouse model study.F1000Res. 2023 Aug 17;12:762. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.136998.3. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 37576540 Free PMC article.
-
Review Article: Night Shift Work, Circadian Disruption, and the Gut Microbiome: Implications for Human Health.Crit Rev Oncog. 2025;30(2):67-81. doi: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2025059579. Crit Rev Oncog. 2025. PMID: 40561433 Review.
-
The molecular circadian clock of eosinophils: a potential therapeutic target for asthma.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 May 1;328(5):C1394-C1408. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00149.2025. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40131242 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Disruption and Prostate Cancer Risk: An Updated Review of Epidemiological Evidences.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017 Jul;26(7):985-991. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-1030. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017. PMID: 28377415
Cited by
-
Uncoupled redox stress: how a temporal misalignment of redox-regulated processes and circadian rhythmicity exacerbates the stressed state.Open Biol. 2023 Sep;13(9):230151. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230151. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 37669692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Shift Work and Health Outcomes in the General Population in China: A Cross-Sectional Study.Brain Sci. 2024 Jan 30;14(2):145. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14020145. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38391721 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between long-term night shift work and incidence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a prospective cohort study of 277,059 UK Biobank participants.BMC Med. 2024 Jan 16;22(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03240-8. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 38225649 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian clock gene expression: a key player in inflammation underlying chronic lung disease?ERJ Open Res. 2025 May 6;11(3):01066-2024. doi: 10.1183/23120541.01066-2024. eCollection 2025 May. ERJ Open Res. 2025. PMID: 40337334 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Clock Deregulation and Metabolic Reprogramming: A System Biology Approach to Tissue-Specific Redox Signaling and Disease Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 28;26(13):6267. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136267. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650041 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akerstedt T Sleepiness as a Consequence of Shift Work. Sleep. 1988;11(1):17–34. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Choi S, Kim K, Park H, Kim KH, Park SM. Association between misalignment of circadian rhythm and obesity in Korean men: Sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Chronobiol Int. 2020;37(2):272–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

