Stiff matrix induces exosome secretion to promote tumour growth
- PMID: 36797475
- PMCID: PMC10351222
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-023-01092-1
Stiff matrix induces exosome secretion to promote tumour growth
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Stiff matrix induces exosome secretion to promote tumour growth.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Mar;26(3):490-491. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01375-1. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38347184 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
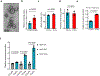
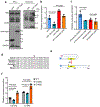
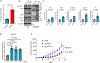
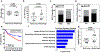
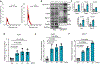
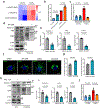
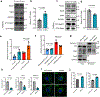
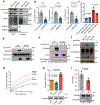
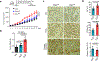
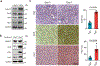
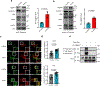
Tissue fibrosis and extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffening promote tumour progression. The mechanisms by which ECM regulates its contacting cells have been extensively studied. However, how stiffness influences intercellular communications in the microenvironment for tumour progression remains unknown. Here we report that stiff ECM stimulates the release of exosomes from cancer cells. We delineate a molecular pathway that links stiff ECM to activation of Akt, which in turn promotes GTP loading to Rab8 that drives exosome secretion. We further show that exosomes generated from cells grown on stiff ECM effectively promote tumour growth. Proteomic analysis revealed that the Notch signalling pathway is activated in cells treated with exosomes derived from tumour cells grown on stiff ECM, consistent with our gene expression analysis of liver tissues from patients. Our study reveals a molecular mechanism that regulates exosome secretion and provides insight into how mechanical properties of the ECM control the tumour microenvironment for tumour growth.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Niche tension controls exosome production.Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Mar;25(3):377-378. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01088-x. Nat Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36797474 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I & Donato F Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology 127, S35–50 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

