Endoscopic stapedotomy: classic versus reversal technique
- PMID: 36797512
- PMCID: PMC10313534
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-023-07880-7
Endoscopic stapedotomy: classic versus reversal technique
Abstract
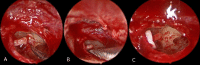
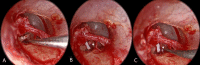
Objectives: To compare hearing outcome and surgical complications between endoscopic classic and reversal stapedotomies.
Patients and methods: A prospective single blinded randomized clinical study carried out on 60 patients with otosclerosis who were randomized into two groups; each containing 30 patients. Patients in group 1 underwent endoscopic classic stapedotomy. Patients in group 2 underwent endoscopic reversal stapedotomy. Both groups were compared as regards hearing outcome and surgical complications.
Results: The difference in the hearing outcome between the two groups was statistically non-significant. Post-operative closure of the air bone gap (ABG) within 10 dB was attained in 76.67% and 80% of patients in groups 1 and 2, respectively. The differences in the surgical complications between the two studied groups were statistically non-significant.
Conclusion: Endoscopic classic and reversal stapedotomies are comparable to each other as regards hearing outcome and surgical complications. The authors recommend further studies with relatively larger sample size.
Keywords: Classic; Endoscopic; Reversal; Stapedotomy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they had no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surgical findings and long-term hearing results in 3,050 stapedotomies for primary otosclerosis: a prospective study with the otology-neurotology database.Otol Neurotol. 2006 Dec;27(8 Suppl 2):S25-47. doi: 10.1097/01.mao.0000235311.80066.df. Otol Neurotol. 2006. PMID: 16985478
-
Classic and reversal steps stapedotomy performed with CO2 laser: a comparative analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 May;271(5):981-6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2500-6. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014. PMID: 23612954
-
Diode Laser Stapedotomy vs Conventional Stapedotomy in Otosclerosis: A Double-Blinded Randomized Clinical Trial.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Jun;154(6):1099-105. doi: 10.1177/0194599816635132. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016. PMID: 26980905 Clinical Trial.
-
Laser vs drill for footplate fenestration during stapedotomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of hearing results.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Jan;278(1):9-14. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06117-1. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 32535861
-
Endoscopic Versus Microscopic Stapedotomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 Apr;172(4):1164-1176. doi: 10.1002/ohn.1109. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 39749405
Cited by
-
Techniques for otosclerosis surgery: Ear surgery from the microscope to the endoscope - A literature review.J Otol. 2024 Apr;19(2):120-126. doi: 10.1016/j.joto.2024.04.002. Epub 2024 Oct 19. J Otol. 2024. PMID: 39720114 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kürsten R, Schneider B, Zrunek M. Long-term results after stapedectomy versus stapedotomy. Am J Otol. 1994;15:804–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

