Implementation of Guidelines on Family Involvement for Persons with Psychotic Disorders (IFIP): A Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36797515
- PMCID: PMC9934504
- DOI: 10.1007/s10488-023-01255-0
Implementation of Guidelines on Family Involvement for Persons with Psychotic Disorders (IFIP): A Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Implementation of Guidelines on Family Involvement for Persons with Psychotic Disorders (IFIP): A Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial.Adm Policy Ment Health. 2023 Nov;50(6):1010-1012. doi: 10.1007/s10488-023-01291-w. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2023. PMID: 37610592 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
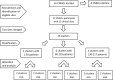
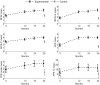
Family involvement is part of the evidence-based treatment for persons with psychotic disorders, yet is under-implemented despite guideline recommendations. This study assessed whether an implementation support programme increased the adherence to guidelines on family involvement, compared to guideline/manual only. In a cluster randomised design, community mental health centre units in South-East Norway went through stratified allocation to the experimental (n = 7) or control (n = 7) arm. Experimental clusters received an implementation support programme including clinical training and supervision, appointing a family coordinator and an implementation team, a toolkit, and fidelity measurements at baseline, 12, 18, and 24 months with on-site feedback and supervision. Control clusters received no such support and had fidelity measurements at baseline and 24 months without feedback. During fidelity measurements, adherence to the guidelines was measured with the basic family involvement and support scale, the general organizational index, and the family psychoeducation fidelity scale, the latter being the primary outcome. The scales consist of 12-14 items rated from 1 to 5. Data was analysed with an independent samples t-test, linear mixed models, and a tobit regression model. At 24 months, the mean scores were 4.00 or higher on all scales in the experimental arm, and the increase in adherence to the guidelines was significantly greater than in the control arm with p-values < 0.001. Large-scale implementation of guidelines on family involvement for persons with psychotic disorders in community mental health centres may be accomplished, with substantial implementation support.Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT03869177. Registered 11.03.19.
Keywords: Family involvement; Family psychoeducation; Fidelity scale; Guideline implementation; Mental health services; Psychotic disorders.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Abma TA. The practice and politics of responsive evaluation. American Journal of Evaluation. 2006;27(1):31–43. doi: 10.1177/1098214005283189. - DOI
-
- Bighelli I, Rodolico A, García-Mieres H, Pitschel-Walz G, Hansen WP, Schneider-Thoma J, Leucht S. Psychosocial and psychological interventions for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2021;8(11):969–980. doi: 10.1016/s2215-0366(21)00243-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bond GR, Drake RE, McHugo GJ, Rapp CA, Whitley R. Strategies for improving fidelity in the national evidence-based practices project. Research on Social Work Practice. 2009;19(5):569–581. doi: 10.1177/1049731509335531. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

