Herbal Therapeutics for Alzheimer's Disease: Ancient Indian Medicine System from the Modern Viewpoint
- PMID: 36797613
- PMCID: PMC10227917
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X21666230216094353
Herbal Therapeutics for Alzheimer's Disease: Ancient Indian Medicine System from the Modern Viewpoint
Abstract
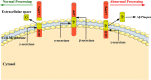
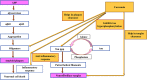
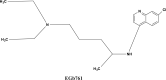
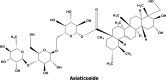
Alzheimer's is a chronic neurodegenerative disease where amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are formed inside the brain. It is also characterized by progressive memory loss, depression, neuroinflammation, and derangement of other neurotransmitters. Due to its complex etiopathology, current drugs have failed to completely cure the disease. Natural compounds have been investigated as an alternative therapy for their ability to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD). Traditional herbs and formulations which are used in the Indian ayurvedic system are rich sources of antioxidant, anti-amyloidogenic, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory compounds. They promote quality of life by improving cognitive memory and rejuvenating brain functioning through neurogenesis. A rich knowledge base of traditional herbal plants (Turmeric, Gingko, Ashwagandha, Shankhpushpi, Giloy, Gotu kola, Garlic, Tulsi, Ginger, and Cinnamon) combined with modern science could suggest new functional leads for Alzheimer's drug discovery. In this article Ayurveda, the ancient Indian herbal medicine system based on multiple clinical and experimental, evidence have been reviewed for treating AD and improving brain functioning. This article presents a modern perspective on the herbs available in the ancient Indian medicine system as well as their possible mechanisms of action for AD treatment. The main objective of this research is to provide a systematic review of herbal drugs that are easily accessible and effective for the treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's; Aβ plaques; cognitive memory; medicinal herbs; neurodegenerative; neurofibrillary tangles.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Traditional Ayurvedic and herbal remedies for Alzheimer's disease: from bench to bedside.Expert Rev Neurother. 2019 May;19(5):359-374. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2019.1596803. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Expert Rev Neurother. 2019. PMID: 30884983 Review.
-
Scientific basis for the use of Indian ayurvedic medicinal plants in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders: ashwagandha.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010 Sep 1;10(3):238-46. doi: 10.2174/1871524911006030238. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20528765 Review.
-
Neuroprotective Herbs for the Management of Alzheimer's Disease.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 8;11(4):543. doi: 10.3390/biom11040543. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33917843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indian Medicinal Herbs and Formulations for Alzheimer's Disease, from Traditional Knowledge to Scientific Assessment.Brain Sci. 2020 Dec 10;10(12):964. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10120964. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33321899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural products against Alzheimer's disease: Pharmaco-therapeutics and biotechnological interventions.Biotechnol Adv. 2017 Mar-Apr;35(2):178-216. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.12.005. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Biotechnol Adv. 2017. PMID: 28043897 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential Role of Phytochemicals in Alzheimer's Disease.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 12;17(4):653. doi: 10.3390/nu17040653. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40004981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in multi-omics research to address challenges in Alzheimer's disease: a systems biology approach utilizing molecular biomarkers and innovative strategies.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Jul 23;17:1591796. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1591796. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40771197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute and Repeated Ashwagandha Supplementation Improves Markers of Cognitive Function and Mood.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 8;16(12):1813. doi: 10.3390/nu16121813. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38931168 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Inhibition of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs) and NF-κB Underlies the Neuroprotective Capacity of a Cinnamon/Curcumin/Turmeric Spice Blend in Aβ-Exposed THP-1 Cells.Molecules. 2023 Dec 5;28(24):7949. doi: 10.3390/molecules28247949. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138438 Free PMC article.
-
Major heme proteins hemoglobin and myoglobin with respect to their roles in oxidative stress - a brief review.Front Chem. 2025 Feb 25;13:1543455. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1543455. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40070406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wenk G.L. Neuropathologic changes in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2003;64(Suppl. 9):7–10. - PubMed
-
- Ferri C.P., Prince M., Brayne C., Brodaty H., Fratiglioni L., Ganguli M., Hall K., Hasegawa K., Hendrie H., Huang Y., Jorm A., Mathers C., Menezes P.R., Rimmer E., Scazufca M. Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet. 2005;366(9503):2112–2117. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67889-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brookmeyer R., Johnson E., Ziegler-Grahamm K., Arrighi H.M. O1-02-01: Forecasting the global prevalence and burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2007;3(3S_Part_3):S168-S168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

