Inadvertent intrathecal drug injection while treating low back pain: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 36797753
- PMCID: PMC9935243
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-023-03754-y
Inadvertent intrathecal drug injection while treating low back pain: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Undesired intrathecal injections represent an important subset of medical errors, albeit rare. Clinical effects depend on the type and concentration of drug(s) injected. Here we report on the case of a healthy woman with persistent low back pain, treated with a paravertebral injection of lidocaine, thiocolchicoside, and L-acetylcarnitine at an orthopedic practice.
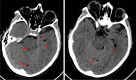
Case report: A 42-year-old Caucasian woman, with no relevant past medical history, received a lumbar paravertebral injection of lidocaine, thiocolchicoside, and L-acetylcarnitine for persistent low back pain. Approximately 30 minutes after injection, she experienced quick neurological worsening. Upon arrival at the Emergency Department, she was comatose, with fixed bilateral mydriasis, trismus, and mixed acidosis; seizures ensued in the first hours; slow progressive amelioration was observed by day 6; retrograde amnesia was the only clinical relevant remaining symptom by 6 months.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of inadvertent intrathecal thiocolchicoside injection in an adult patient, as well as the first in the neurosurgical literature. Our experience suggests that injection therapy for low back pain should be administered in adequate settings, where possible complications may be promptly treated.
Keywords: Chemical meningo-encephalitis; Intrathecal administration; Undesired intrathecal injections.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this manuscript content.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous