Arabidopsis sepals: A model system for the emergent process of morphogenesis
- PMID: 36798428
- PMCID: PMC9931181
- DOI: 10.1017/qpb.2021.12
Arabidopsis sepals: A model system for the emergent process of morphogenesis
Abstract
During development, Arabidopsis thaliana sepal primordium cells grow, divide and interact with their neighbours, giving rise to a sepal with the correct size, shape and form. Arabidopsis sepals have proven to be a good system for elucidating the emergent processes driving morphogenesis due to their simplicity, their accessibility for imaging and manipulation, and their reproducible development. Sepals undergo a basipetal gradient of growth, with cessation of cell division, slow growth and maturation starting at the tip of the sepal and progressing to the base. In this review, I discuss five recent examples of processes during sepal morphogenesis that yield emergent properties: robust size, tapered tip shape, laminar shape, scattered giant cells and complex gene expression patterns. In each case, experiments examining the dynamics of sepal development led to the hypotheses of local rules. In each example, a computational model was used to demonstrate that these local rules are sufficient to give rise to the emergent properties of morphogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest. The author declares none.
Figures
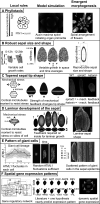
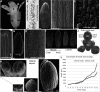
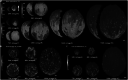
References
-
- Ambrose, B. A. , Lerner, D. R. , Ciceri, P. , Padilla, C. M. , Yanofsky, M. F. , & Schmidt, R. J. (2000). Molecular and genetic analyses of the Silky1 gene reveal conservation in floral organ specification between eudicots and monocots. Molecular Cell, 5, 569–579. - PubMed
-
- Antoniou Kourounioti, R. L. , Band, L. R. , Fozard, J. A. , Hampstead, A. , Lovrics, A. , Moyroud, E. , Vignolini, S. , King, J. R. , Jensen, O. E. , & Glover, B. J. (2012). Buckling as an origin of ordered cuticular patterns in flower petals. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 10, 20120847. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barbier de Reuille, P. , Routier-Kierzkowska, A.-L. , Kierzkowski, D. , Bassel, G. W. , Schüpbach, T. , Tauriello, G. , Bajpai, N. , Strauss, S. , Weber, A. , Kiss, A. , Burian, A. , Hofhuis, H. , Sapala, A. , Lipowczan, M. , Heimlicher, M. B. , Robinson, S. , Bayer, E. M. , Basler, K. , Koumoutsakos, P. , Roeder, A. H. , … Smith, R. S. (2015). MorphoGraphX: A platform for quantifying morphogenesis in 4D. eLife, 4, e05864. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Besnard, F. , Refahi, Y. , Morin, V. , Marteaux, B. , Brunoud, G. , Chambrier, P. , Rozier, F. , Mirabet, V. , Legrand, J. , Lainé, S. , Thévenon, E. , Farcot, E. , Cellier, C. , Das, P. , Bishopp, A. , Dumas, R. , Parcy, F. , Helariutta, Y. , Boudaoud, A. , Godin, C. , … Vernoux, T. (2014). Cytokinin signalling inhibitory fields provide robustness to phyllotaxis. Nature, 505, 417–421. - PubMed
-
- Bichet, A. , Desnos, T. , Turner, S. , Grandjean, O. , & Höfte, H. (2001). BOTERO1 is required for normal orientation of cortical microtubules and anisotropic cell expansion in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 25, 137–148. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
