ARMS-NF-κB signaling regulates intracellular ROS to induce autophagy-associated cell death upon oxidative stress
- PMID: 36798436
- PMCID: PMC9926119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106005
ARMS-NF-κB signaling regulates intracellular ROS to induce autophagy-associated cell death upon oxidative stress
Abstract
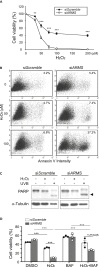
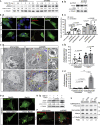
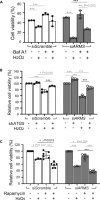
Ankyrin repeat-rich membrane spanning (ARMS) plays roles in neural development, neuropathies, and tumor formation. Such pleiotropic function of ARMS is often attributed to diverse ARMS-interacting molecules in different cell context. However, it might be achieved by ARMS' effect on global biological mediator like reactive oxygen species (ROS). We established ARMS-knockdown in melanoma cells (siARMS) and in Drosophila eyes (GMR>dARMS RNAi ) and challenged them with H2O2. Decreased ARMS in both systems compromises nuclear translocation of NF-κB and induces ROS, which in turn augments autophagy flux and confers susceptibility to H2O2-triggered autophagic cell death. Resuming NF-κB activity or reducing ROS by antioxidants in siARMS cells and GMR>dARMS RNAi fly decreases intracellular peroxides level concurrent with reduced autophagy and attenuated cell death. Conversely, blocking NF-κB activity in wild-type flies/melanoma enhances ROS and induces autophagy with cell death. We thus uncover intracellular ROS modulated by ARMS-NFκB signaling primes autophagy for autophagic cell death upon oxidative stress.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Cell biology; Molecular biology.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We report no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physalin A induces apoptosis via p53-Noxa-mediated ROS generation, and autophagy plays a protective role against apoptosis through p38-NF-κB survival pathway in A375-S2 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jul 9;148(2):544-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.04.051. Epub 2013 May 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23684722
-
Inhibiting ROS-NF-κB-dependent autophagy enhanced brazilin-induced apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Mar;101:55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28063998
-
NF-κB activation was involved in reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis and autophagy in 1-oxoeudesm-11(13)-eno-12,8α-lactone-treated human lung cancer cells.Arch Pharm Res. 2014 Aug;37(8):1039-52. doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0270-8. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Arch Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24194260
-
Bidirectional regulation of NF-κB by reactive oxygen species: a role of unfolded protein response.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:162-174. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.020. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23792277 Review.
-
Interactions between reactive oxygen species and autophagy: Special issue: Death mechanisms in cellular homeostasis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021 Jul;1868(8):119041. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2021.119041. Epub 2021 Apr 17. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 33872672 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Insights into the Role of UV Radiation-Induced Oxidative Stress in Melanoma Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 30;25(21):11651. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111651. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chenopodium botrys Extract Affects Acute Kidney Injury Caused by Rhabdomyolysis in Rats Through TNF/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Dec 10;13(1):e4667. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4667. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39803217 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

