Low-density lipoprotein: a versatile nanoscale platform for targeted delivery
- PMID: 36798503
- PMCID: PMC9926902
- DOI: 10.1039/d2na00883a
Low-density lipoprotein: a versatile nanoscale platform for targeted delivery
Abstract
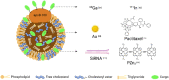
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is a small lipoprotein that plays a vital role in controlling lipid metabolism. LDL has a delicate nanostructure with unique physicochemical properties: superior payload capacity, long residence time in circulation, excellent biocompatibility, smaller size, and natural targeting. In recent decades, the superiority and feasibility of LDL particles as targeted delivery carriers have attracted much attention. In this review, we introduce the structure, composition, advantages, defects, and reconstruction of LDL delivery systems, summarize their research status and progress in targeted diagnosis and therapy, and finally look forward to the clinical application of LDL as an effective delivery vehicle.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Preparation of Lipid Nanodisks Containing Apolipoprotein E-Derived Synthetic Peptides for Biocompatible Delivery Vehicles Targeting Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor.Biol Pharm Bull. 2019;42(8):1376-1383. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00287. Biol Pharm Bull. 2019. PMID: 31366872
-
Enhanced blood-brain barrier penetration and glioma therapy mediated by T7 peptide-modified low-density lipoprotein particles.Drug Deliv. 2018 Nov;25(1):1652-1663. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2018.1494223. Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 30394123 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic lipoprotein as nano-material vehicle in the targeted drug delivery.Drug Deliv. 2017 Dec;24(sup1):16-21. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1384518. Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 29069931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-density lipoprotein-mediated drug delivery system.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Nov 15;106(Pt A):132-147. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.04.030. Epub 2016 May 18. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 27208399 Review.
-
Low-density lipoprotein nanomedicines: mechanisms of targeting, biology, and theranostic potential.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):408-421. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1886199. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 33594923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevention of Colitis-Associated Cancer via Oral Administration of M13-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 16;15(9):2331. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092331. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765299 Free PMC article.
-
Photodynamic Therapy and Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 4;25(5):2974. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052974. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipoprotein receptors: A little grease for enveloped viruses to open the lock?J Biol Chem. 2024 Nov;300(11):107849. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107849. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39357828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Hotspots and Development Trends on Apolipoprotein B in the Field of Atherosclerosis: A Bibliometric Analysis.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun;67(6):2204-2222. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01218-2. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38963531 Review.

