Intramuscular mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 induces neutralizing salivary IgA
- PMID: 36798518
- PMCID: PMC9927016
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.933347
Intramuscular mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 induces neutralizing salivary IgA
Abstract
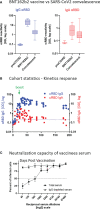
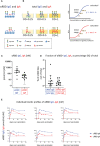
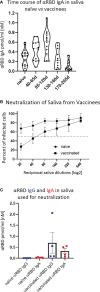
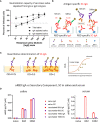
Intramuscularly administered vaccines stimulate robust serum neutralizing antibodies, yet they are often less competent in eliciting sustainable "sterilizing immunity" at the mucosal level. Our study uncovers a strong temporary neutralizing mucosal component of immunity, emanating from intramuscular administration of an mRNA vaccine. We show that saliva of BNT162b2 vaccinees contains temporary IgA targeting the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 spike protein and demonstrate that these IgAs mediate neutralization. RBD-targeting IgAs were found to associate with the secretory component, indicating their bona fide transcytotic origin and their polymeric multivalent nature. The mechanistic understanding of the high neutralizing activity provided by mucosal IgA, acting at the first line of defense, will advance vaccination design and surveillance principles and may point to novel treatment approaches and new routes of vaccine administration and boosting.
Keywords: BNT162b2 vaccine; SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing Abs; mucosal immunity; secretory IgA; secretory component.
Copyright © 2023 Stolovich-Rain, Kumari, Friedman, Kirillov, Socol, Billan, Pal, Das, Golding, Oiknine-Djian, Sirhan, Sagie, Cohen-Kfir, Gold, Fahoum, Kumar, Elgrably-Weiss, Zhou, Ravins, Gatt, Bhattacharya, Zelig, Wiener, Wolf, Elinav, Strahilevitz, Padawer, Baraz and Rouvinski.
Conflict of interest statement
Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center and Hadassah Academic College has filed a patent application “Compounds and methods for increasing antibody’s neutralization properties and methods for assessing antibody response” on which MSR, SuK, AF, PG, RW, DP, LB, and AR are listed as inventors. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

