Graph analysis of diffusion tensor imaging-based connectome in young men with internet gaming disorder
- PMID: 36798605
- PMCID: PMC9926964
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1090224
Graph analysis of diffusion tensor imaging-based connectome in young men with internet gaming disorder
Abstract
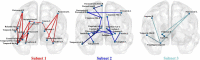
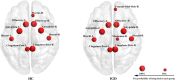
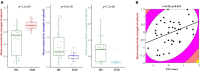
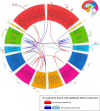
Although recent evidence suggests that dysfunctional brain organization is associated with internet gaming disorder (IGD), the neuroanatomical alterations related to IGD remain unclear. In this diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) study, we aimed to examine alterations in white matter (WM) structural connectomes and their association with IGD characteristics in 47 young men with IGD and in 34 well-matched healthy controls. Two approaches [namely, network-based statistics (NBS) and graph theoretical measures] were applied to assess differences in the specific topological features of the networks and to identify the potential changes in the topological properties, respectively. Furthermore, we explored the association between the alterations and the severity of internet addiction. An NBS analysis revealed widespread alterations of the cortico-limbic-striatal structural connectivity networks in young people with IGD: (1) an increased subnet1 comprising the insula and the regions responsible for visual, auditory, and sensorimotor functions and (2) two decreased subnet2 and subnet3 comprising the insula, striatum, and limbic regions. Additional correlation analysis showed a significant positive association between the mean fractional anisotropy- (FA-) weighted connectivity strength of subnet1 and internet addiction test (IAT) scores in the IGD group. The present study extends our knowledge of the neuroanatomical correlates in IGD and highlights the role of the cortico-limbic-striatal network in understanding the neurobiological mechanisms underlying this disorder.
Keywords: DTI; connectome; cortico-limbic-striatal network; internet gaming disorder; structural connectivity.
Copyright © 2023 Qin, Wang, Ni, Wu, Chen, Guo, Zhang, Zhou and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The topological organization of white matter network in internet gaming disorder individuals.Brain Imaging Behav. 2017 Dec;11(6):1769-1778. doi: 10.1007/s11682-016-9652-0. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017. PMID: 27815774
-
White matter connectivity and Internet gaming disorder.Addict Biol. 2016 May;21(3):732-42. doi: 10.1111/adb.12246. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Addict Biol. 2016. PMID: 25899390 Free PMC article.
-
Internet gaming disorder: deficits in functional and structural connectivity in the ventral tegmental area-Accumbens pathway.Brain Imaging Behav. 2019 Aug;13(4):1172-1181. doi: 10.1007/s11682-018-9929-6. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019. PMID: 30054871
-
Large-scale network dysfunction in youths with Internet gaming disorder: a meta-analysis of resting-state functional connectivity studies.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 13;109:110242. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110242. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33434637 Review.
-
Graph theory approach for the structural-functional brain connectome of depression.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Dec 20;111:110401. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110401. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34265367 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential scalp acupuncture and brain stimulation targets for common neurological disorders: evidence from neuroimaging studies.Chin Med. 2025 May 7;20(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01106-0. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40329319 Free PMC article.
-
EEG Microstate Analysis in Patients with Disorders of Consciousness and Its Clinical Significance.Brain Topogr. 2024 May;37(3):377-387. doi: 10.1007/s10548-023-00939-y. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Brain Topogr. 2024. PMID: 36735192
-
Automatic Classification of Emotions Based on Cardiac Signals: A Systematic Literature Review.Ann Biomed Eng. 2023 Nov;51(11):2393-2414. doi: 10.1007/s10439-023-03341-8. Epub 2023 Aug 5. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 37543539 Review.
-
First performance evaluation of easyPET.3D, a high-resolution and cost-effective benchtop preclinical PET scanner.EJNMMI Phys. 2025 May 26;12(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s40658-025-00757-0. EJNMMI Phys. 2025. PMID: 40418258 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics-based machine learning atherosclerotic carotid artery disease in ultrasound: systematic review with meta-analysis of RQS.J Ultrasound. 2025 Jun 9. doi: 10.1007/s40477-025-01002-1. Online ahead of print. J Ultrasound. 2025. PMID: 40489053
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association [APA]. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5™, 5th Edn. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.
-
- Bax T. (2015). “Internet gaming disorder” in China: biomedical sickness or sociological badness? Games Cult. 11 233–255. 10.1177/1555412014568188 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

