Expression, regulating mechanism and therapeutic target of KIF20A in multiple cancer
- PMID: 36798768
- PMCID: PMC9925975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13195
Expression, regulating mechanism and therapeutic target of KIF20A in multiple cancer
Abstract
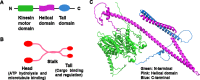
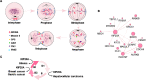
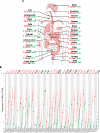
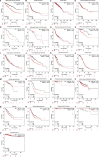
Kinesin family member 20A (KIF20A) is a member of the kinesin family. It transports chromosomes during mitosis, plays a key role in cell division. Recently, studies proved that KIF20A was highly expressed in cancer. High expression of KIF20A was correlated with poor overall survival (OS). In this review, we summarized all the cancer that highly expressed KIF20A, described the role of KIF20A in cancer. We also organized phase I and phase II clinical trials of KIF20A peptides vaccine. All results indicated that KIF20A was a promising therapeutic target for multiple cancer.
Keywords: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; BTC, biliary tract cancer; CPC, chromosomal passenger complex; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; Cancer; Cdk1, cyclin-dependent kinase 1; DLG5, discs large MAGUK scaffold protein 5; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Expression; FoxM1, forkhead box protein M1; GC, gastric cancer; GEM, gemcitabine; Gli2, glioma-associated oncogene 2; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; HNMT, head-and-neck malignant tumor; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; JAK, Janus kinase; KIF20A; KIF20A, kinesin family member 20A; LP, long peptide; MHC I, major histocompatibility complex I; MKlp2, mitotic kinesin-like protein 2; Mad2, mitotic arrest deficient 2; OS, overall survival; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; Plk1, polo-like kinase 1; Regulating mechanisms; Therapeutic target; circRNA, circular RNA; miRNA, microRNA.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hirokawa N., Noda Y. Intracellular transport and kinesin superfamily proteins, KIFs: structure, function, and dynamics. Physiol. Rev. 2008;88(3):1089–1118. - PubMed
-
- Oki E., et al. Clinical aspect and molecular mechanism of DNA aneuploidy in gastric cancers. J. Gastroenterol. 2012;47(4):351–358. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

