Thrombin generation and implications for hemophilia therapies: A narrative review
- PMID: 36798897
- PMCID: PMC9926221
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpth.2022.100018
Thrombin generation and implications for hemophilia therapies: A narrative review
Abstract
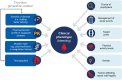
Thrombin plays an essential role in achieving and maintaining effective hemostasis and stable clot formation. In people with hemophilia, deficiency of procoagulant factor (F)VIII or FIX results in insufficient thrombin generation, leading to reduced clot stability and various bleeding manifestations. A correlation has been found between the bleeding phenotype of people with hemophilia and the extent of thrombin generation, with individuals with increased thrombin generation being protected from bleeding and those with lower thrombin generation having increased bleeding tendency. The amount, location, and timing of thrombin generation have been found to affect the formation and stability of the resulting clot. The goal of all therapies for hemophilia is to enhance the generation of thrombin with the aim of restoring effective hemostasis and preventing or controlling bleeding; current treatment approaches rely on either replacing or mimicking the missing procoagulant (ie, FVIII or FIX) or rebalancing hemostasis through lowering natural anticoagulants, such as antithrombin. Global coagulation assays, such as the thrombin generation assay, may help guide the overall management of hemostasis by measuring and monitoring the hemostatic potential of patients and, thus, assessing the efficacy of treatment in people with hemophilia. Nevertheless, standardization of the thrombin generation assay is needed before it can be adopted in routine clinical practice.
Keywords: antithrombins; blood coagulation tests; fitusiran; hemophilia; hemostasis; therapies.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures

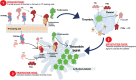


 = unstable hemostasis (due to peaks and troughs in factor levels);
= unstable hemostasis (due to peaks and troughs in factor levels);  = very stable hemostasis (with no peaks and troughs in factor levels);
= very stable hemostasis (with no peaks and troughs in factor levels);  = peaks and troughs in factor levels;
= peaks and troughs in factor levels;  = no direct impact on factor levels (activated prothrombin complex concentrate mimics prothrombin to enhance thrombin generation, rFVIIa targets and enhances thrombin generation, and nonfactor therapies impact on and target stable hemostasis rather than factor levels). ETP, endogenous thrombin potential; F, factor; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; TGA, thrombin generation assay. aPostinfusion values. bTime to peak increased after dose after reaching steady state after 4 weeks of loading doses and in the maintenance phase of treatment [52]
= no direct impact on factor levels (activated prothrombin complex concentrate mimics prothrombin to enhance thrombin generation, rFVIIa targets and enhances thrombin generation, and nonfactor therapies impact on and target stable hemostasis rather than factor levels). ETP, endogenous thrombin potential; F, factor; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; TGA, thrombin generation assay. aPostinfusion values. bTime to peak increased after dose after reaching steady state after 4 weeks of loading doses and in the maintenance phase of treatment [52]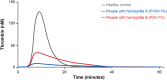
References
-
- Negrier C., Shima M., Hoffman M. The central role of thrombin in bleeding disorders. Blood Rev. 2019;38 - PubMed
-
- Bolton-Maggs P.H., Pasi K.J. Haemophilias A and B. Lancet. 2003;361:1801–1809. - PubMed
-
- Dargaud Y., Béguin S., Lienhart A., Al Dieri R., Trzeciak C., Bordet J.C., et al. Evaluation of thrombin generating capacity in plasma from patients with haemophilia A and B. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93:475–480. - PubMed
-
- Livnat T., Sehgal A., Qian K., Van Nguyen H., Madigan K., Sorensen B., et al. Thrombin generation in plasma of patients with haemophilia A and B with inhibitors: effects of bypassing agents and antithrombin reduction. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020;82 - PubMed
-
- Makris M., Hermans C. A golden age for haemophilia treatment? Haemophilia. 2018;24:175–176. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

