Effect of miR‑29a‑3p in exosomes on glioma cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT/HIF‑1α pathway
- PMID: 36799154
- PMCID: PMC9942261
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2023.12959
Effect of miR‑29a‑3p in exosomes on glioma cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT/HIF‑1α pathway
Abstract
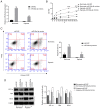
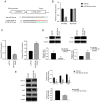
Exosomes secreted by glioma cells can carry a number of bioactive molecules. As the most abundant noncoding RNA in exosomes, microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in signaling between tumor cells in a number of ways. In addition, hypoxia is an important feature of the microenvironment of most tumors. The present study investigated the effect of miR‑29a‑3p in glioma exosomes on the proliferation and apoptosis levels of U251 glioma cells under hypoxia. Qualitative PCR results showed that the expression level of miR‑29a‑3p in plasma exosomes of glioma patients was lower than that of normal subjects. By conducting hypoxia experiments in vitro on U251 glioma cells, it was found that the expression level of miR‑29a‑3p decreased following hypoxia, while overexpression of miR‑29a‑3p significantly decreased the proliferation of U251 glioma cells and promoted apoptosis by inhibiting the expression of the antiapoptotic marker Bcl‑2 and increasing the expression of the proapoptotic marker Bax The potential targets of miR‑29a‑3p were predicted by online tools and validated by a dual‑luciferase gene reporter assay. miR‑29a‑3p was found to target and regulate PI3K, which in turn inhibited the activity of the PI3K‑AKT pathway, thereby reducing the expression of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)‑1α protein. Furthermore, the effects of miR‑29a‑3p on proliferation and apoptosis in glioma cells in those processes could be reversed by the PI3K‑AKT agonist Recilisib. In addition, the inhibitory effect of miR‑29a‑3p on the PI3K/AKT/HIF‑1α regulatory axis could cause a decrease in the expression levels of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase‑1 and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase‑2 and eventually lead to a reduction in glycolysis in U251 glioma cells. Similarly, Recilisib slowed the inhibitory effect of miR‑29a‑3p on glycolysis and glycolysis‑related molecules. The results of this study tentatively confirm that miR‑29a‑3p carried by exosomes can be used as a novel diagnostic marker and a potential inhibitory molecule for glioma cells, providing a new theoretical and experimental basis for the precise clinical treatment of glioma.
Keywords: exosome; glioma; hypoxia inducible factor 1α; microRNA 29a‑3p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


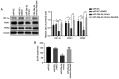
Similar articles
-
Cinnamaldehyde Downregulation of Sept9 Inhibits Glioma Progression through Suppressing Hif-1α via the Pi3k/Akt Signaling Pathway.Dis Markers. 2022 Jan 19;2022:6530934. doi: 10.1155/2022/6530934. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35096204 Free PMC article.
-
miR-489 inhibits proliferation, cell cycle progression and induces apoptosis of glioma cells via targeting SPIN1-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:435-443. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.058. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28666210
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00152/miR-613/CD164 axis regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in glioma via PI3K/AKT pathway.Neoplasma. 2020 Jul;67(4):762-772. doi: 10.4149/neo_2020_190706N598. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Neoplasma. 2020. PMID: 32726126
-
Biological, diagnostic and therapeutic implications of exosomes in glioma.Cancer Lett. 2024 Feb 1;582:216592. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216592. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Cancer Lett. 2024. PMID: 38092145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of Exosomes as Future Therapeutic Agents and Diagnostic Tools for Glioma.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 13;11:733529. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.733529. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34722277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Connection between Radiation-Regulating Functions of Natural Products and miRNAs Targeting Radiomodulation and Exosome Biogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 4;24(15):12449. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512449. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes-mediated crosstalk between glioma and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Aug;29(8):2074-2085. doi: 10.1111/cns.14239. Epub 2023 May 11. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 37170647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astaxanthin suppresses the malignant behaviors of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by blocking PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pathways via miR-29a-3p.Genes Environ. 2024 Apr 22;46(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s41021-024-00304-w. Genes Environ. 2024. PMID: 38649975 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma-Derived Exosomal i-tRF-LeuCAA as Biomarker for Glioma Diagnosis and Promoter of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via TPM4 Regulation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Apr;31(4):e70356. doi: 10.1111/cns.70356. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40202170 Free PMC article.
-
The signature of extracellular vesicles in hypoxic breast cancer and their therapeutic engineering.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 21;22(1):512. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01870-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39434182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

