Modulating epigenetic modifications for cancer therapy (Review)
- PMID: 36799181
- PMCID: PMC9942256
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2023.8496
Modulating epigenetic modifications for cancer therapy (Review)
Abstract
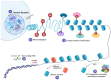
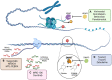
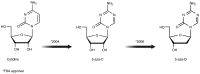
Cancer is a global public health concern. Alterations in epigenetic processes are among the earliest genomic aberrations occurring during cancer development and are closely related to progression. Unlike genetic mutations, aberrations in epigenetic processes are reversible, which opens the possibility for novel pharmacological treatments. Non‑coding RNAs (ncRNAs) represent an essential epigenetic mechanism, and emerging evidence links ncRNAs to carcinogenesis. Epigenetic drugs (epidrugs) are a group of promising target therapies for cancer treatment acting as coadjuvants to reverse drug resistance in cancer. The present review describes central epigenetic aberrations during malignant transformation and explains how epidrugs target DNA methylation, histone modifications and ncRNAs. Furthermore, clinical trials focused on evaluating the effect of these epidrugs alone or in combination with other anticancer therapies and other ncRNA‑based therapies are discussed. The use of epidrugs promises to be an effective tool for reversing drug resistance in some patients with cancer.
Keywords: cancer; epigenetic drugs; epigenetic mechanisms; non‑coding RNA; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

