GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Induce Growth Hormone Secretion in Healthy Volunteers
- PMID: 36800161
- PMCID: PMC10064408
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-023-01381-w
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Induce Growth Hormone Secretion in Healthy Volunteers
Abstract
Introduction: Growth hormone (GH) is an essential regulator of growth, body composition and fuel metabolism and, consequently, GH secretion is under the feedback control of numerous nutritional and endocrine mediators. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have been shown to exert pleiotropic effects, including stimulation of the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. As GLP-1RAs exert multiple metabolic effects, we hypothesised that they may also affect the secretion of GH and examined the effect of a short-acting and a long-acting GLP-1 RA on GH secretion.
Methods: This is a post hoc analysis of data from clinical trials. Two separate single-group open-label clinical trials were carried out in the ambulatory care setting with a duration of 1 and 21 days, respectively. Healthy adult male and female volunteers with no chronic illnesses or use of daily medicines were recruited for the study. The two interventions were: study 1, single dose of 10 µg exenatide administered subcutaneously (s.c.); study 2, 0.6 mg liraglutide administered s.c. once daily for 21 days.
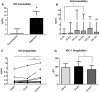
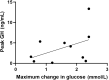
Results: Administration of a single dose of exenatide (study 1) caused a clear increase in GH levels, peaking between 60 and 120 min post-administration. There was also a small but statistically significant decrease in luteinising hormone and testosterone levels 120 min after exenatide dosing. Administration of the long-acting GLP-1RA liraglutide daily for 21 days (study 2) elicited an increase in GH levels with no change in insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentrations after 3 weeks of treatment.
Conclusions: The results show that the administration of GLP-1RAs may elicit an increase in growth hormone levels. GLP-1 signalling may be a novel mechanism of regulation of GH secretion. This finding needs to be replicated in the placebo-controlled trial.
Clinical trial registration numbers: NCT02089256 and NCT03160261.
Keywords: Exenatide; GLP-1 receptor agonist; Growth hormone.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Marathe CS, Pham H, Wu T, et al. Acute administration of the GLP-1 receptor agonist lixisenatide diminishes postprandial insulin secretion in healthy subjects but not in type 2 diabetes, associated with slowing of gastric emptying. Diabetes Ther. 2022;13:1245–1249. doi: 10.1007/s13300-022-01258-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nair R, Mody R, Yu M, et al. Real-world treatment patterns of glucose-lowering agents among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease or at risk for cardiovascular disease: an observational, cross-sectional. Retrospect Study Diabet Ther. 2022;13:1921–1932. doi: 10.1007/s13300-022-01320-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

