In vivo HSC prime editing rescues sickle cell disease in a mouse model
- PMID: 36800642
- PMCID: PMC10163316
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022018252
In vivo HSC prime editing rescues sickle cell disease in a mouse model
Abstract
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a monogenic disease caused by a nucleotide mutation in the β-globin gene. Current gene therapy studies are mainly focused on lentiviral vector-mediated gene addition or CRISPR/Cas9-mediated fetal globin reactivation, leaving the root cause unfixed. We developed a vectorized prime editing system that can directly repair the SCD mutation in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in vivo in a SCD mouse model (CD46/Townes mice). Our approach involved a single intravenous injection of a nonintegrating, prime editor-expressing viral vector into mobilized CD46/Townes mice and low-dose drug selection in vivo. This procedure resulted in the correction of ∼40% of βS alleles in HSCs. On average, 43% of sickle hemoglobin was replaced by adult hemoglobin, thereby greatly mitigating the SCD phenotypes. Transplantation in secondary recipients demonstrated that long-term repopulating HSCs were edited. Highly efficient target site editing was achieved with minimal generation of insertions and deletions and no detectable off-target editing. Because of its simplicity and portability, our in vivo prime editing approach has the potential for application in resource-poor countries where SCD is prevalent.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.L. and H.-P.K. are academic co-founders of Ensoma Therapeutics. H.P.K. is a paid advisor for Ensoma. P.J.C. is currently an employee of Prime Medicine. D.R.L. is a consultant for Prime Medicine, Beam Therapeutics, Pairwise Plants, Chroma Medicine, and Nvelop Therapeutics, companies that use or deliver genome editing or epigenome engineering agents, and owns equity in these companies. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
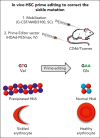
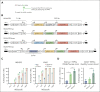
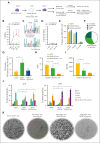

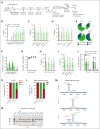

Comment in
-
The promise of in vivo HSC prime editing.Blood. 2023 Apr 27;141(17):2039-2040. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023019922. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37103948 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kato GJ, Piel FB, Reid CD, et al. Sickle cell disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4 - PubMed
-
- Kanter J, Walters MC, Krishnamurti L, et al. Biologic and clinical efficacy of LentiGlobin for sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(7):617–628. - PubMed
-
- Frangoul H, Altshuler D, Cappellini MD, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing for sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):252–260. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

