Repression of the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor prevents oxidative stress and ferroptosis of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes
- PMID: 36801011
- PMCID: PMC10101911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.01.023
Repression of the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor prevents oxidative stress and ferroptosis of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes
Abstract
The aryl-hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that buoys intestinal immune responses. AHR induces its own negative regulator, the AHR repressor (AHRR). Here, we show that AHRR is vital to sustaining intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs). AHRR deficiency reduced IEL representation in a cell-intrinsic fashion. Single-cell RNA sequencing revealed an oxidative stress profile in Ahrr-/- IELs. AHRR deficiency unleashed AHR-induced expression of CYP1A1, a monooxygenase that generates reactive oxygen species, increasing redox imbalance, lipid peroxidation, and ferroptosis in Ahrr-/- IELs. Dietary supplementation with selenium or vitamin E to restore redox homeostasis rescued Ahrr-/- IELs. Loss of IELs in Ahrr-/- mice caused susceptibility to Clostridium difficile infection and dextran sodium-sulfate-induced colitis. Inflamed tissue of inflammatory bowel disease patients showed reduced Ahrr expression that may contribute to disease. We conclude that AHR signaling must be tightly regulated to prevent oxidative stress and ferroptosis of IELs and to preserve intestinal immune responses.
Keywords: AHRR; Ahr; Cyp1a1; IBD; IEL; ROS; ferroptosis; mucosal immunity; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M. Colonna receives research support from Pfizer.
Figures
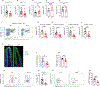




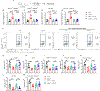

Comment in
-
Negative regulation of AHR essential for intestinal homeostasis.Nat Rev Immunol. 2023 Apr;23(4):202. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00852-2. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36849743 No abstract available.
References
-
- Van Kaer L, Algood HMS, Singh K, Parekh VV, Greer MJ, Piazuelo MB, Weitkamp JH, Matta P, Chaturvedi R, Wilson KT, and Olivares-Villagomez D (2014). CD8alphaalpha(+) innate-type lymphocytes in the intestinal epithelium mediate mucosal immunity. Immunity 41, 451–464. S1074–7613(14)00304–5 [pii]10.1016/j.immuni.2014.08.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

