Innexin-Mediated Adhesion between Glia Is Required for Axon Ensheathment in the Peripheral Nervous System
- PMID: 36801823
- PMCID: PMC10072304
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1323-22.2023
Innexin-Mediated Adhesion between Glia Is Required for Axon Ensheathment in the Peripheral Nervous System
Abstract
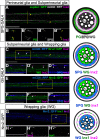
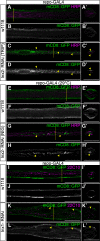
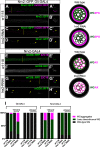
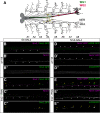
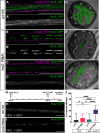
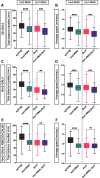
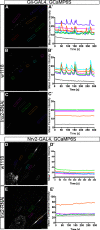
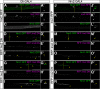
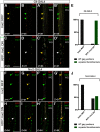
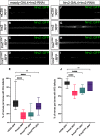
Glia are essential to protecting and enabling nervous system function and a key glial function is the formation of the glial sheath around peripheral axons. Each peripheral nerve in the Drosophila larva is ensheathed by three glial layers, which structurally support and insulate the peripheral axons. How peripheral glia communicate with each other and between layers is not well established and we investigated the role of Innexins in mediating glial function in the Drosophila periphery. Of the eight Drosophila Innexins, we found two (Inx1 and Inx2) are important for peripheral glia development. In particular loss of Inx1 and Inx2 resulted in defects in the wrapping glia leading to disruption of the glia wrap. Of interest loss of Inx2 in the subperineurial glia also resulted in defects in the neighboring wrapping glia. Inx plaques were observed between the subperineurial glia and the wrapping glia suggesting that gap junctions link these two glial cell types. We found Inx2 is key to Ca2+ pulses in the peripheral subperineurial glia but not in the wrapping glia, and we found no evidence of gap junction communication between subperineurial and wrapping glia. Rather we have clear evidence that Inx2 plays an adhesive and channel-independent role between the subperineurial and wrapping glia to ensure the integrity of the glial wrap.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Gap junctions are critical for glia communication and formation of myelin in myelinating glia. However, the role of gap junctions in non-myelinating glia is not well studied, yet non-myelinating glia are critical for peripheral nerve function. We found the Innexin gap junction proteins are present between different classes of peripheral glia in Drosophila. Here Innexins form junctions to facilitate adhesion between the different glia but do so in a channel-independent manner. Loss of adhesion leads to disruption of the glial wrap around axons and leads to fragmentation of the wrapping glia membranes. Our work points to an important role for gap junction proteins in mediating insulation by non-myelinating glia.
Keywords: gap junction; glia; innexin; insulation.
Copyright © 2023 the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Axonal wrapping in the Drosophila PNS is controlled by glia-derived neuregulin homolog Vein.Development. 2015 Apr 1;142(7):1336-45. doi: 10.1242/dev.116616. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Development. 2015. PMID: 25758464
-
Innexins Ogre and Inx2 are required in glial cells for normal postembryonic development of the Drosophila central nervous system.J Cell Sci. 2013 Sep 1;126(Pt 17):3823-34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.117994. Epub 2013 Jun 26. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23813964
-
Expression of a dominant negative mutant innexin in identified neurons and glial cells reveals selective interactions among gap junctional proteins.Dev Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;73(8):571-86. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22082. Epub 2013 May 14. Dev Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23447124
-
Gap junction communication in myelinating glia.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1828(1):69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.01.024. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22326946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glial ensheathment of peripheral axons in Drosophila.J Neurosci Res. 2008 May 1;86(6):1189-98. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21574. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18041093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dendrite intercalation between epidermal cells tunes nociceptor sensitivity to mechanical stimuli in Drosophila larvae.PLoS Genet. 2024 Apr 25;20(4):e1011237. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011237. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38662763 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Pathways Controlling Axonal Wrapping in Drosophila.Cells. 2023 Oct 31;12(21):2553. doi: 10.3390/cells12212553. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37947631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Drosophila blood-brain barrier invades the nervous system in a GPCR-dependent manner.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 May 23;18:1397627. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1397627. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38846639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauer R, Loer B, Ostrowski K, Martini J, Weimbs A, Lechner H, Hoch M (2005) Intercellular communication: the Drosophila innexin multiprotein family of gap junction proteins. Chem Biol 12:515–526. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ (2006) Calcium microdomains: organization and function. Cell Calcium 40:405–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
