Early postnatal defects in neurogenesis in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36801910
- PMCID: PMC9938901
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-05650-1
Early postnatal defects in neurogenesis in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
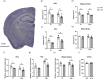
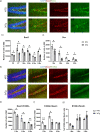
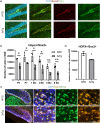
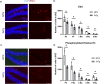
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder leading to dementia. The hippocampus, which is one of the sites where neural stem cells reside and new neurons are born, exhibits the most significant neuronal loss in AD. A decline in adult neurogenesis has been described in several animal models of AD. However, the age at which this defect first appears remains unknown. To determine at which stage, from birth to adulthood, the neurogenic deficits are found in AD, we used the triple transgenic mouse model of AD (3xTg). We show that defects in neurogenesis are present as early as postnatal stages, well before the onset of any neuropathology or behavioral deficits. We also show that 3xTg mice have significantly fewer neural stem/progenitor cells, with reduced proliferation and decreased numbers of newborn neurons at postnatal stages, consistent with reduced volumes of hippocampal structures. To determine whether there are early changes in the molecular signatures of neural stem/progenitor cells, we perform bulk RNA-seq on cells sorted directly from the hippocampus. We show significant changes in the gene expression profiles at one month of age, including genes of the Notch and Wnt pathways. These findings reveal impairments in neurogenesis very early in the 3xTg AD model, which provides new opportunities for early diagnosis and therapeutic interventions to prevent neurodegeneration in AD.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dysregulated expression of monoacylglycerol lipase is a marker for anti-diabetic drug metformin-targeted therapy to correct impaired neurogenesis and spatial memory in Alzheimer's disease.Theranostics. 2020 May 15;10(14):6337-6360. doi: 10.7150/thno.44962. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32483456 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread deficits in adult neurogenesis precede plaque and tangle formation in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Neurosci. 2010 Sep;32(6):905-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07379.x. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Eur J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20726889
-
Selenomethionine promoted hippocampal neurogenesis via the PI3K-Akt-GSK3β-Wnt pathway in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Mar 25;485(1):6-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.069. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28109879
-
Therapeutic potential of neurogenesis for prevention and recovery from Alzheimer's disease: allopregnanolone as a proof of concept neurogenic agent.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006 Jul;3(3):185-90. doi: 10.2174/156720506777632817. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006. PMID: 16842093 Review.
-
Neural stem cells and adult brain fatty acid metabolism: Lessons from the 3xTg model of Alzheimer's disease.Biol Cell. 2018 Jan;110(1):6-25. doi: 10.1111/boc.201700037. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 28980327 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in adult and aged genetically diverse mice.Geroscience. 2025 Jun 17. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01749-9. Online ahead of print. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 40526250
-
Alzheimer's Amyloid-β Accelerates Cell Senescence and Suppresses SIRT1 in Human Neural Stem Cells.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 4;14(2):189. doi: 10.3390/biom14020189. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397428 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Stem Cell's Perspective.Cells. 2025 Feb 27;14(5):347. doi: 10.3390/cells14050347. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40072076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Oct;20(10):7369-7383. doi: 10.1002/alz.14179. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39166771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical-grade human dental pulp stem cells improve adult hippocampal neural regeneration and cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease.Theranostics. 2025 Jan 1;15(3):894-914. doi: 10.7150/thno.102315. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 39776809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moreno-Jiménez EP, Flor-García M, Terreros-Roncal J, Rábano A, Cafini F, Pallas-Bazarra N, et al. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med. 2019;25:554–60. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0375-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

