Assessing attitudes towards insulin pump therapy in adults with type 1 diabetes: Italian validation of the Insulin Pump Attitudes Questionnaire (IT-IPA questionnaire)
- PMID: 36801976
- PMCID: PMC10063466
- DOI: 10.1007/s00592-023-02046-7
Assessing attitudes towards insulin pump therapy in adults with type 1 diabetes: Italian validation of the Insulin Pump Attitudes Questionnaire (IT-IPA questionnaire)
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Assessing attitudes towards insulin pump therapy in adults with type 1 diabetes: Italian validation of the Insulin Pump Attitudes Questionnaire (IT‑IPA questionnaire).Acta Diabetol. 2023 Jul;60(7):1005. doi: 10.1007/s00592-023-02090-3. Acta Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37083963 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Aims: The aim of the study was to adapt the German version of the insulin pump therapy (IPA) questionnaire to Italian (IT-IPA) and to evaluate its psychometric properties in adults with type 1 diabetes.
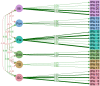
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study, data were collected through an online survey. In addition to IT-IPA, questionnaires evaluating depression, anxiety, diabetes distress, self-efficacy, and treatment satisfaction were administered. The six factors identified in the IPA German version were assessed using confirmatory factor analysis; psychometric testing included construct validity and internal consistency.
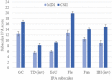
Results: The online survey was compiled by 182 individuals with type 1 diabetes: 45.6% continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) users and 54.4% multiple daily insulin injection users. The six-factor model had a very good fit in our sample. The internal consistency was acceptable (Cronbach's α = 0.75; 95% IC [0.65-0.81]). Diabetes treatment satisfaction was positively correlated with a positive attitude towards CSII therapy (Spearman's rho = 0.31; p < 0.01), less Technology Dependency, higher Ease of Use, and less Impaired Body Image. Furthermore, less Technology Dependency was associated with lower diabetes distress and depressive symptoms.
Conclusions: The IT-IPA is a valid and reliable questionnaire evaluating attitudes towards insulin pump therapy. The questionnaire can be used for clinical practice during consultations for shared decision-making to CSII therapy.
Keywords: Attitudes; Insulin pump therapy; Psychometric validation; Psychosocial aspects; Type 1 diabetes.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nicolucci A, Maione A, Franciosi M, Amoretti R, Busetto E, Capani F, et al. Quality of life and treatment satisfaction in adults with Type 1 diabetes: a comparison between continuous subcuta- neous insulin infusion and multiple daily injections. Diabet Med. 2008;25:213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02346.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shaban C, Knott J, Jenkins E, Weiss M, Ryder J, Charman J, Partridge H. Diabetes distress and fear of hypoglycaemia: what are the psychological benefits of insulin pump therapy? Practical Diabetes. 2017;34(8):273–276. doi: 10.1002/pdi.2135. - DOI
-
- Bonora E, Sesti G, Società Italiana di Diabetologia (2016) Il diabete in Italia. Bononia University Press. https://www.siditalia.it/pdf/Il%20Diabete%20in%20Italia_p.pdf Accessed January 25, 2022
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

