Anesthetic management of a patient with methamphetamine-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- PMID: 36801985
- PMCID: PMC9939558
- DOI: 10.1186/s40981-023-00601-3
Anesthetic management of a patient with methamphetamine-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Abstract
Background: Methamphetamine abuse is a serious public health concern and causes various life-threatening disorders including pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Herein, we present the first case report describing the anesthetic management of a patient with methamphetamine-associated PAH (M-A PAH) undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
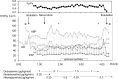
Case presentation: A 34-year-old female with M-A PAH suffered from deterioration of right ventricular (RV) heart failure due to recurrent cholecystitis and was scheduled for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Preoperative assessment of PA pressure showed 82/32 (mean, 50) mmHg, and transthoracic echocardiology revealed a slight reduction of RV function. General anesthesia was induced and maintained by thiopental, remifentanil, sevoflurane, and rocuronium. PA pressure gradually increased after peritoneal insufflation; therefore, we administered dobutamine and nitroglycerin to decrease pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR). The patient emerged from anesthesia smoothly.
Conclusions: Avoiding increased PVR by appropriate anesthesia and medical hemodynamic support is an important consideration for patients with M-A PAH.
Keywords: Methamphetamine; Peritoneal insufflation; Pulmonary arterial hypertension; Pulmonary artery catheter; Right ventricular dysfunction.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Xu R, Zhao SX. Current state and understanding of methamphetamine-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur J Respir Med. 2021;3(1):167–171.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
