MicroRNA-122 in human cancers: from mechanistic to clinical perspectives
- PMID: 36803831
- PMCID: PMC9940444
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-023-02868-z
MicroRNA-122 in human cancers: from mechanistic to clinical perspectives
Abstract
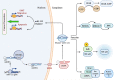
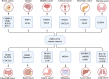
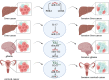
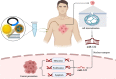
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous short non-coding RNAs that can regulate the expression of target genes post-transcriptionally and interact with mRNA-coding genes. MiRNAs play vital roles in many biological functions, and abnormal miRNA expression has been linked to various illnesses, including cancer. Among the miRNAs, miR-122, miR-206, miR-21, miR-210, miR-223, and miR-424 have been extensively studied in various cancers. Although research in miRNAs has grown considerably over the last decade, much is yet to be discovered, especially regarding their role in cancer therapies. Several kinds of cancer have been linked to dysregulation and abnormal expression of miR-122, indicating that miR-122 may serve as a diagnostic and/or prognostic biomarker for human cancer. Consequently, in this review literature, miR-122 has been analyzed in numerous cancer types to sort out the function of cancer cells miR-122 and enhance patient response to standard therapy.
Keywords: Cancer; Pathogenesis; Prognosis; Therapy; miR-122.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shirvani H, Ghanavi J, Aliabadi A, Mousavinasab F, Talebi M, Majidpoor J, et al. MiR-211 plays a dual role in cancer development: from tumor suppressor to tumor enhancer. Cell Signal. 2023;101:110504. - PubMed
-
- Khasraghi LB, Nouri M, Vazirzadeh M, Hashemipour N, Talebi M, Zarch FA, et al. MicroRNA-206 in human cancer: mechanistic and clinical perspectives. Cell Signal. 2023;101:110525. - PubMed
-
- Dehghani M, Zarch SMA, Mehrjardi MYV, Nazari M, Babakhanzadeh E, Ghadimi H, et al. Evaluation of miR-181b and miR-126-5p expression levels in T2DM patients compared to healthy individuals: relationship with NF-κB gene expression. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. 2020;67(7):454–460. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

