Prediction and Demonstration of Retinoic Acid Receptor Agonist Ch55 as an Antifibrotic Agent in the Dermis
- PMID: 36804965
- PMCID: PMC10432574
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.01.024
Prediction and Demonstration of Retinoic Acid Receptor Agonist Ch55 as an Antifibrotic Agent in the Dermis
Abstract
The prevalence of fibrotic diseases and the lack of pharmacologic modalities to effectively treat them impart particular importance to the discovery of novel antifibrotic therapies. The repurposing of drugs with existing mechanisms of action and/or clinical data is a promising approach for the treatment of fibrotic diseases. One paradigm that pervades all fibrotic diseases is the pathological myofibroblast, a collagen-secreting, contractile mesenchymal cell that is responsible for the deposition of fibrotic tissue. In this study, we use a gene expression paradigm characteristic of activated myofibroblasts in combination with the Connectivity Map to select compounds that are predicted to reverse the pathological gene expression signature associated with the myofibroblast and thus contain the potential for use as antifibrotic compounds. We tested a small list of these compounds in a first-pass screen, applying them to fibroblasts, and identified the retinoic acid receptor agonist Ch55 as a potential hit. Further investigation exhibited and elucidated the antifibrotic effects of Ch55 in vitro as well as showing antiscarring activity upon intradermal application in a preclinical rabbit ear hypertrophic scar model. We hope that similar predictions to uncover antiscarring compounds may yield further preclinical and ultimately clinical success.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
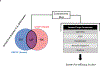

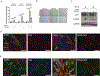
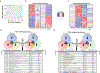
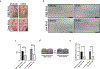
Comment in
-
Targeting Myofibroblasts in Dermal Fibrosis: A Retinoid Connection.J Invest Dermatol. 2023 Sep;143(9):1629-1631. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.03.1663. Epub 2023 Apr 26. J Invest Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37115114 No abstract available.
References
-
- Abbasi S, Sinha S, Labit E, Rosin NL, Yoon G, Rahmani W, et al. Distinct regulatory programs control the latent regenerative potential of dermal fibroblasts during wound healing. Cell stem cell 2020;27(3):396–412. e6. - PubMed
-
- Abergel RP, Meeker CA, Oikarinen H, Oikarinen AI, Uitto J. Retinoid modulation of connective tissue metabolism in keloid fibroblast cultures. Arch Dermatol 1985;121(5):632–5. - PubMed
-
- Al Tanoury Z, Piskunov A, Andriamoratsiresy D, Gaouar S, Lutzing R, Ye T, et al. Genes involved in cell adhesion and signaling: a new repertoire of retinoic acid receptor target genes in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Journal of Cell Science 2014;127(3):521–33. - PubMed
-
- Amiri N, Golin AP, Jalili RB, Ghahary A. Roles of cutaneous cell-cell communication in wound healing outcome: An emphasis on keratinocyte-fibroblast crosstalk. Experimental Dermatology 2022;31(4):475–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

