Brain-constrained neural modeling explains fast mapping of words to meaning
- PMID: 36807501
- PMCID: PMC10233283
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhad007
Brain-constrained neural modeling explains fast mapping of words to meaning
Abstract
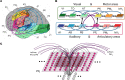
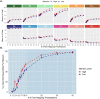
Although teaching animals a few meaningful signs is usually time-consuming, children acquire words easily after only a few exposures, a phenomenon termed "fast-mapping." Meanwhile, most neural network learning algorithms fail to achieve reliable information storage quickly, raising the question of whether a mechanistic explanation of fast-mapping is possible. Here, we applied brain-constrained neural models mimicking fronto-temporal-occipital regions to simulate key features of semantic associative learning. We compared networks (i) with prior encounters with phonological and conceptual knowledge, as claimed by fast-mapping theory, and (ii) without such prior knowledge. Fast-mapping simulations showed word-specific representations to emerge quickly after 1-10 learning events, whereas direct word learning showed word-meaning mappings only after 40-100 events. Furthermore, hub regions appeared to be essential for fast-mapping, and attention facilitated it, but was not strictly necessary. These findings provide a better understanding of the critical mechanisms underlying the human brain's unique ability to acquire new words rapidly.
Keywords: Hebbian learning; biologically neural networks; distributed neural assemblies; fast mapping; language acquisition; semantic grounding.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Adams SV, Wennekers T, Cangelosi A, Garagnani M, Pulvermüller F. 2014. Learning visual-motor cell assemblies for the iCub robot using a neuroanatomically grounded neural network. In: 2014 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence, Cognitive Algorithms, Mind, and Brain (CCMB). Presented at the 2014 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence, Cognitive Algorithms, Mind, and Brain (CCMB). p. 1–8.
-
- Amir Y, Harel M, Malach R. Cortical hierarchy reflected in the organization of intrinsic connections in macaque monkey visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1993:334(1):19–46. - PubMed
-
- Arikuni T, Watanabe K, Kubota K. Connections of area 8 with area 6 in the brain of the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1988:277(1):21–40. - PubMed
-
- Artola A, Singer W. Long-term depression of excitatory synaptic transmission and its relationship to long-term potentiation. Trends Neurosci. 1993:16(11):480–487. - PubMed
-
- Artola A, Bröcher S, Singer W. Different voltage-dependent thresholds for inducing long-term depression and long-term potentiation in slices of rat visual cortex. Nature. 1990:347(6288):69–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

