Treatment Strategy for Rifampin-Susceptible Tuberculosis
- PMID: 36808186
- PMCID: PMC7616851
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2212537
Treatment Strategy for Rifampin-Susceptible Tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: Tuberculosis is usually treated with a 6-month rifampin-based regimen. Whether a strategy involving shorter initial treatment may lead to similar outcomes is unclear.
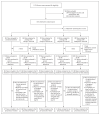
Methods: In this adaptive, open-label, noninferiority trial, we randomly assigned participants with rifampin-susceptible pulmonary tuberculosis to undergo either standard treatment (rifampin and isoniazid for 24 weeks with pyrazinamide and ethambutol for the first 8 weeks) or a strategy involving initial treatment with an 8-week regimen, extended treatment for persistent clinical disease, monitoring after treatment, and retreatment for relapse. There were four strategy groups with different initial regimens; noninferiority was assessed in the two strategy groups with complete enrollment, which had initial regimens of high-dose rifampin-linezolid and bedaquiline-linezolid (each with isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol). The primary outcome was a composite of death, ongoing treatment, or active disease at week 96. The noninferiority margin was 12 percentage points.
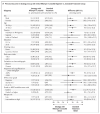
Results: Of the 674 participants in the intention-to-treat population, 4 (0.6%) withdrew consent or were lost to follow-up. A primary-outcome event occurred in 7 of the 181 participants (3.9%) in the standard-treatment group, as compared with 21 of the 184 participants (11.4%) in the strategy group with an initial rifampin-linezolid regimen (adjusted difference, 7.4 percentage points; 97.5% confidence interval [CI], 1.7 to 13.2; noninferiority not met) and 11 of the 189 participants (5.8%) in the strategy group with an initial bedaquiline-linezolid regimen (adjusted difference, 0.8 percentage points; 97.5% CI, -3.4 to 5.1; noninferiority met). The mean total duration of treatment was 180 days in the standard-treatment group, 106 days in the rifampin-linezolid strategy group, and 85 days in the bedaquiline-linezolid strategy group. The incidences of grade 3 or 4 adverse events and serious adverse events were similar in the three groups.
Conclusions: A strategy involving initial treatment with an 8-week bedaquiline-linezolid regimen was noninferior to standard treatment for tuberculosis with respect to clinical outcomes. The strategy was associated with a shorter total duration of treatment and with no evident safety concerns. (Funded by the Singapore National Medical Research Council and others; TRUNCATE-TB ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03474198.).
Copyright © 2023 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
In TB, an 8-wk, 5-drug regimen was noninferior to a standard 24-wk, 4-drug regimen for clinical outcomes at 96 wk.Ann Intern Med. 2023 Jun;176(6):JC64. doi: 10.7326/J23-0036. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Ann Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37276602
-
Treatment Strategy for Rifampin-Susceptible Tuberculosis.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jun 15;388(24):2296-2297. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2304776. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37314714 No abstract available.
-
Treatment Strategy for Rifampin-Susceptible Tuberculosis.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jun 15;388(24):2297. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2304776. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37314715 No abstract available.
-
Treatment Strategy for Rifampin-Susceptible Tuberculosis.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jun 15;388(24):2297-2298. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2304776. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37314716 No abstract available.
-
Treatment Strategy for Rifampin-Susceptible Tuberculosis. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jun 15;388(24):2298. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2304776. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37314717 No abstract available.
References
-
- Global tuberculosis report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. Oct 14, ( https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021)
-
- WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis: module 4: treatment: drug-susceptible tuberculosis treatment. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022. May 24, ( https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240048126) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
