Radiographic methods for locating impacted maxillary canines
- PMID: 36808194
- PMCID: PMC10026925
- DOI: 10.47162/RJME.63.4.01
Radiographic methods for locating impacted maxillary canines
Abstract
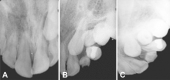
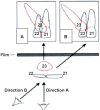
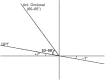
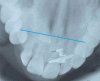
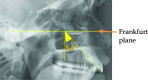
Maxillary canine impaction is a fairly common phenomenon in dental practice. Most studies indicate its palatal position. For a successful orthodontic and∕or surgical therapy, it is necessary to correctly identify the impacted canine in the depth of the maxillary bone, using conventional and digital radiological investigations, each with their advantages and disadvantages. Dental practitioners must indicate the most "targeted" radiological investigation. This paper aims to review the various radiographic techniques available for determining the location of the impacted maxillary canine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures





References
-
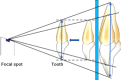
- Akan S, Oktay H. Cone beam tomography and panoramic radiography in localization of impacted maxillary canine and detection of root resorption. Stoma Edu J. 2021;8(2):106–112.
-
- El Beshlawy. Radiographic assessment of impacted maxillary canine position using CBCT: a comparative study of 2 methods. Egypt Dent J. 2019;65(4):3393–3402.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

