Evaluation of YouTube Videos on Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 36808545
- PMCID: PMC9941019
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e50
Evaluation of YouTube Videos on Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: As in every field, online information has become increasingly used in health. However, it is well known that some information online containing health advice is incorrect and may even include false statements. For this reason, it is crucial for public health that individuals reach reliable, high-quality resources when they are trying to obtain health information. Studies have been conducted on the quality and reliability of online information about many diseases, but no similar study has been found in the literature on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
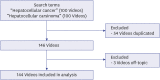
Methods: In this descriptive study, videos on YouTube (www.youtube.com) about HCC were evaluated using the Global Quality Scale (GQS) and the modified DISCERN tool.
Results: While 129 (89.58%) of the videos examined within the study were considered useful, 15 (10.42%) were misleading. The GQS scores of the videos considered useful were significantly higher than the scores of the misleading videos, with a median (min-max) score of 4 (2-5) (P < 0.001). When we compared the DISCERN scores, the scores of the useful videos were significantly higher (P < 0.001) than the scores of the misleading videos.
Conclusion: YouTube should be considered a complex structure where accurate and reliable health information can be presented, as well as erroneous and misleading information. Users should understand the importance of video sources and focus their research on videos from doctors, academics, and universities.
Keywords: Education; Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Quality of Information; YouTube.
© 2023 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Similar articles
-
The efficacy and reliability of English YouTube videos as a source of information for pregnant rheumatoid arthritis patients.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Dec;42(12):3311-3320. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06780-9. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37814092
-
The Quality, Reliability, and Popularity of YouTube Education Videos for Vestibular Rehabilitation: A Cross-sectional Study.Otol Neurotol. 2021 Sep 1;42(8):e1077-e1083. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003197. Otol Neurotol. 2021. PMID: 34028400
-
Quality of English-language videos on YouTube as a source of information on systemic lupus erythematosus.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Dec;23(12):1636-1644. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13852. Epub 2020 May 13. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32406201
-
YouTube as a source of information on systemic sclerosis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2022 Aug;25(8):887-892. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14363. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Int J Rheum Dis. 2022. PMID: 35666007
-
Is the information about orthodontics on Youtube and TikTok reliable for the oral health of the public? A cross sectional comparative study.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022 Oct;123(5):e349-e354. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2022.04.009. Epub 2022 Apr 22. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022. PMID: 35470122
Cited by
-
YouTube as a source of information for stroke rehabilitation: a cross-sectional analysis of quality and reliability of videos.Rheumatol Int. 2025 Mar 22;45(4):77. doi: 10.1007/s00296-025-05832-4. Rheumatol Int. 2025. PMID: 40119932 Free PMC article.
-
The quality and reliability of short videos about thyroid nodules on BiliBili and TikTok: Cross-sectional study.Digit Health. 2024 Oct 7;10:20552076241288831. doi: 10.1177/20552076241288831. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39381823 Free PMC article.
-
YouTube as a Source of Information on Public Health Ethics.J Korean Med Sci. 2024 Feb 26;39(7):e61. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e61. J Korean Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38412608 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Quality and Reliability of YouTube as a Source of Information on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Call to Publish More Quality Videos by Professionals.J Korean Med Sci. 2025 Apr 7;40(13):e34. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2025.40.e34. J Korean Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40195923 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the quality and reliability of YouTube videos related to teleradiology in musculoskeletal and rheumatic diseases: a cross-sectional study.Rheumatol Int. 2025 Mar 14;45(4):74. doi: 10.1007/s00296-025-05831-5. Rheumatol Int. 2025. PMID: 40085231 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials