Ribavirin Treatment Failure-Associated Mutation, Y1320H, in the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase of Genotype 3 Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Enhances Virus Replication in a Rabbit HEV Infection Model
- PMID: 36809085
- PMCID: PMC10128057
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.03372-22
Ribavirin Treatment Failure-Associated Mutation, Y1320H, in the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase of Genotype 3 Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Enhances Virus Replication in a Rabbit HEV Infection Model
Abstract
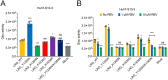
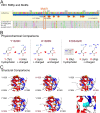
Chronic hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection has become a significant clinical problem that requires treatment in immunocompromised individuals. In the absence of an HEV-specific antiviral, ribavirin (RBV) has been used off-label, but treatment failure may occur due to mutations in the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), including Y1320H, K1383N, and G1634R. Chronic hepatitis E is mostly caused by zoonotic genotype 3 HEV (HEV-3), and HEV variants from rabbits (HEV-3ra) are closely related to human HEV-3. Here, we explored whether HEV-3ra, along with its cognate host, can serve as a model to study RBV treatment failure-associated mutations observed in human HEV-3-infected patients. By utilizing the HEV-3ra infectious clone and indicator replicon, we generated multiple single mutants (Y1320H, K1383N, K1634G, and K1634R) and a double mutant (Y1320H/K1383N) and assessed the role of mutations on replication and antiviral activity of HEV-3ra in cell culture. Furthermore, we also compared the replication of the Y1320H mutant with the wild-type HEV-3ra in experimentally infected rabbits. Our in vitro analyses revealed that the effects of these mutations on rabbit HEV-3ra are altogether highly consistent with those on human HEV-3. Importantly, we found that the Y1320H enhances virus replication during the acute stage of HEV-3ra infection in rabbits, which corroborated our in vitro results showing an enhanced viral replication of Y1320H. Taken together, our data suggest that HEV-3ra and its cognate host is a useful and relevant naturally occurring homologous animal model to study the clinical relevance of antiviral-resistant mutations observed in human HEV-3 chronically-infected patients. IMPORTANCE HEV-3 causes chronic hepatitis E that requires antiviral therapy in immunosuppressed individuals. RBV is the main therapeutic option for chronic hepatitis E as an off-label use. Several amino acid changes, including Y1320H, K1383N, and G1634R, in the RdRp of human HEV-3 have reportedly been associated with RBV treatment failure in chronic hepatitis E patients. In this study, we utilized an HEV-3ra from rabbit and its cognate host to investigate the effect of these RBV treatment failure-associated HEV-3 RdRp mutations on viral replication efficiency and antiviral susceptibility. The in vitro data using rabbit HEV-3ra was highly comparable to those from human HEV-3. We demonstrated that the Y1320H mutation significantly enhanced HEV-3ra replication in cell culture and enhanced virus replication during the acute stage of HEV-3ra infection in rabbits. The rabbit HEV-3ra infection model should be useful in delineating the role of human HEV-3 RBV treatment failure-associated mutations in antiviral resistance.
Keywords: chronic hepatitis E (CHE); genotype 3 HEV (HEV-3); hepatitis E virus (HEV); rabbit HEV-3ra; ribavirin (RBV) treatment failure-associated mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
