MRI-based cephalometrics: a scoping review of current insights and future perspectives
- PMID: 36809112
- PMCID: PMC10304848
- DOI: 10.1259/dmfr.20230024
MRI-based cephalometrics: a scoping review of current insights and future perspectives
Abstract
Objective: This review aims to explore the current status of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a cephalometric tool, summarize the equipment design and methods, and propose recommendations for future research.
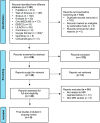
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in electronic databases, including PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, EBSCOhost, LILACS, and Cochrane Library, using broad search terms. The articles published in any language till June 2022 were considered. Cephalometric studies conducted using the MRI dataset on human participants, phantom or cadaver were included. Two independent reviewers assessed the final eligible articles using the quality assessment score (QAS).
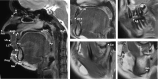
Results: Nine studies were included in the final assessment. Studies used various methods, including 1.5 T or 3 T MRI systems and 3D or 2D MRI datasets. Among the imaging sequences, T1-weighted, T2-weighted and black bone MR images were used for cephalometric analysis. In addition, the reference standards varied among studies, such as traditional 2D cephalogram, cone-beam CT and phantom measurements. The mean QAS of all the included studies was 79% (± 14.4%). The main limitation of most studies was the small sample size and the heterogeneity of the methods, statistical tools used, and metric outcomes assessed.
Conclusions: Despite the heterogeneity and lack of metrological evidence on the effectiveness of MRI-based cephalometric analysis, the preliminary results demonstrated by in vivo and in vitro studies are encouraging. However, future studies exploring MRI sequences specific to cephalometric diagnosis are required for wider adoption of this technique in routine orthodontic practice.
Keywords: cephalometry; diagnostic imaging; magnetic resonance imaging; nonionising radiation; orthodontics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare that they have no competing financial or personal interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kharbanda OP. Orthodontics: Diagnosis and management of malocclusion and dentofacial deformities. In: Kharbanda OP, ed. Cephalometrics: Historical perspectives, methods and landmarks. 3rd ed. New Delhi, India : Elsevier Health Sciences; 2019., : 234
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

