Encouraging brisk walking with the free Active10 app in postnatal women who had a hypertensive pregnancy: "Just Walk It" feasibility study
- PMID: 36809278
- PMCID: PMC9942986
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282066
Encouraging brisk walking with the free Active10 app in postnatal women who had a hypertensive pregnancy: "Just Walk It" feasibility study
Abstract
Objective: To explore the feasibility of a future trial to investigate whether encouraging use of the free NHS smartphone app Active10 increases brisk walking and reduces blood pressure (BP) in postnatal mothers who had hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP).
Design: 3-month feasibility study.
Setting: London maternity unit.
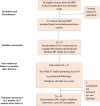
Population: 21 women with HDP.
Methods: At recruitment we recorded initial (booking) clinic BP and asked participants to complete a questionnaire. Two months after delivery all participants were sent (by post/email/WhatsApp) a "Just Walk It" leaflet encouraging them to download the Active10 app and walk briskly for at least 10 minutes/day. This was backed by a telephone call after 2-weeks. Assessments were repeated 3-months later, and included telephone interviews about the acceptability and use of Active10.
Main outcome measures: Were recruitment rate, follow-up rate and acceptability/use of Active10.
Results: Of 28 women approached, 21 (75%, 95% CI 55.1-89.3%) agreed to participate. Age range was 21-46 years and five (24%) self-identified as black ethnicity. One woman dropped out of the study, and one became ill. The remaining participants (90%, 19/21, 95% CI 69.6-98.8%) were followed up after 3-months. Ninety-five percent (18/19) downloaded the Active10 app and 74% (14/19) continued using it at 3-months, averaging 27-minutes brisk walking/day according to Active10 weekly screenshots. Comments included: "Brilliant app", "Really motivates me". Mean BP was 130/81mmHg at booking and 124/80mmHg at 3-months follow-up.
Conclusions: The Active10 app was acceptable to postnatal women after HDP and may have increased minutes of brisk walking. A future trial could explore whether this simple, low-cost intervention could reduce long-term BP in this vulnerable group.
Copyright: © 2023 Razai et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous