CLOCK and TIMELESS regulate rhythmic occupancy of the BRAHMA chromatin-remodeling protein at clock gene promoters
- PMID: 36809369
- PMCID: PMC9983840
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010649
CLOCK and TIMELESS regulate rhythmic occupancy of the BRAHMA chromatin-remodeling protein at clock gene promoters
Abstract
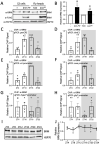
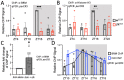
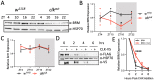
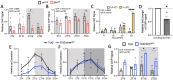
Circadian clock and chromatin-remodeling complexes are tightly intertwined systems that regulate rhythmic gene expression. The circadian clock promotes rhythmic expression, timely recruitment, and/or activation of chromatin remodelers, while chromatin remodelers regulate accessibility of clock transcription factors to the DNA to influence expression of clock genes. We previously reported that the BRAHMA (BRM) chromatin-remodeling complex promotes the repression of circadian gene expression in Drosophila. In this study, we investigated the mechanisms by which the circadian clock feeds back to modulate daily BRM activity. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we observed rhythmic BRM binding to clock gene promoters despite constitutive BRM protein expression, suggesting that factors other than protein abundance are responsible for rhythmic BRM occupancy at clock-controlled loci. Since we previously reported that BRM interacts with two key clock proteins, CLOCK (CLK) and TIMELESS (TIM), we examined their effect on BRM occupancy to the period (per) promoter. We observed reduced BRM binding to the DNA in clk null flies, suggesting that CLK is involved in enhancing BRM occupancy to initiate transcriptional repression at the conclusion of the activation phase. Additionally, we observed reduced BRM binding to the per promoter in flies overexpressing TIM, suggesting that TIM promotes BRM removal from DNA. These conclusions are further supported by elevated BRM binding to the per promoter in flies subjected to constant light and experiments in Drosophila tissue culture in which the levels of CLK and TIM are manipulated. In summary, this study provides new insights into the reciprocal regulation between the circadian clock and the BRM chromatin-remodeling complex.
Copyright: © 2023 Tabuloc et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Catalytic and Non-catalytic Functions of the Brahma Chromatin-Remodeling Protein Collaborate to Fine-Tune Circadian Transcription in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jul 1;11(7):e1005307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005307. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26132408 Free PMC article.
-
CLOCKWORK ORANGE promotes CLOCK-CYCLE activation via the putative Drosophila ortholog of CLOCK INTERACTING PROTEIN CIRCADIAN.Curr Biol. 2021 Oct 11;31(19):4207-4218.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.07.017. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34331859 Free PMC article.
-
CLOCKWORK ORANGE Enhances PERIOD Mediated Rhythms in Transcriptional Repression by Antagonizing E-box Binding by CLOCK-CYCLE.PLoS Genet. 2016 Nov 4;12(11):e1006430. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006430. eCollection 2016 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27814361 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional feedback loop regulation, function, and ontogeny in Drosophila.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:437-44. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2007.72.009. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007. PMID: 18419302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Regulation of Circadian Chromatin.J Mol Biol. 2020 May 29;432(12):3466-3482. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.01.009. Epub 2020 Jan 16. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31954735 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

