Diabetes remission of bariatric surgery and nonsurgical treatments in type 2 diabetes patients who failure to meet the criteria for surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36810013
- PMCID: PMC9945737
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-023-01283-9
Diabetes remission of bariatric surgery and nonsurgical treatments in type 2 diabetes patients who failure to meet the criteria for surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of bariatric surgery in moderate and severe obesity patients to reach diabetes remission is clear, but for mild obesity patients, the choice of surgical and non-surgical treatment is still unclear. This study we aim to compare the effect of surgical and nonsurgical treatment on patients BMI < 35 kg/m2 to reach diabetes remission.
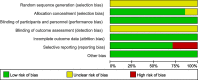
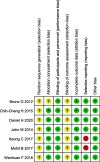
Method: We searched relevant articles publish between Jan 1,2010 and Jan 1, 2023 in the following databases: Embase, PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, and Cochrane Library. We got the OR, MD and P-value using random effect model to compare the efficiency between bariatric surgery and nonsurgical treatment on diabetes remission, the reduction of BMI, Hb1Ac and FPG.
Results: In 7 included studies including 544 participants, bariatric surgery is more effective than non-surgical treatment to reach diabetes remission [OR 25.06, 95%CL 9.58-65.54]. Bariatric surgery more likely resulted in significant reductions in HbA1c [MD -1.44, 95%CL (-1.84)-(-1.04)] and FPG [MD -2.61, 95%CL (-3.20)-(-2.20)]. Bariatric surgery may resulted in reductions in BMI [MD -3.14, 95%CL (-4.41)-(-1.88)], which more significant in Asian.
Conclusion: In type 2 diabetes patients who BMI < 35 kg/m2, bariatric surgery is more likely to achieve diabetes remission and better blood glucose control than nonsurgical treatment.
Keywords: BMI<35kg/m²; Bariatric surgery; Diabetes remission.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
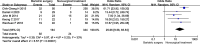

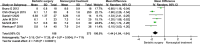
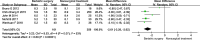
Similar articles
-
Predictors of remission of diabetes mellitus in severely obese individuals undergoing bariatric surgery: do BMI or procedure choice matter? A meta-analysis.Ann Surg. 2015 Mar;261(3):459-67. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000863. Ann Surg. 2015. PMID: 25361217 Review.
-
Predictors of T2DM Remission after Bariatric Surgery in Patients with a BMI < 35 kg/m2: a Meta-Analysis.Obes Surg. 2023 Aug;33(8):2342-2355. doi: 10.1007/s11695-023-06671-7. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Obes Surg. 2023. PMID: 37328645
-
Five-year effectiveness of bariatric surgery on disease remission, weight loss, and changes of metabolic parameters in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: A population-based propensity score-matched cohort study.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020 Mar;36(3):e3236. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3236. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 31912598
-
Bariatric/Metabolic Surgery to Treat Type 2 Diabetes in Patients With a BMI <35 kg/m2.Diabetes Care. 2016 Jun;39(6):924-33. doi: 10.2337/dc16-0350. Diabetes Care. 2016. PMID: 27222550 Free PMC article.
-
Is Bariatric Surgery Effective for Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Body Mass Index < 35 kg/m2? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Obes Surg. 2021 Sep;31(9):4083-4092. doi: 10.1007/s11695-021-05520-9. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Obes Surg. 2021. PMID: 34244912
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Bariatric Surgery in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2023 Oct 27;15(10):e47843. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47843. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021602 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of bariatric surgery on glycemic and metabolic outcomes in people with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-evidence of 39 studies.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 23;12:1603670. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1603670. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40626220 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Remission, Dream or Reality? A Narrative Review of Current Evidence and Integrated Care Strategies.Diabetes Ther. 2025 Aug;16(8):1557-1579. doi: 10.1007/s13300-025-01761-4. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Diabetes Ther. 2025. PMID: 40512404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preoperative duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus and remission after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a single center long-term cohort study.Int J Surg. 2024 Oct 1;110(10):6214-6221. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001139. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38348897 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Key Moments in Type 2 Diabetes Management: A Qualitative Study of the Experiences of People With Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetes Health Coaches.Health Expect. 2024 Dec;27(6):e70108. doi: 10.1111/hex.70108. Health Expect. 2024. PMID: 39572877 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

