Single-cell whole-genome sequencing, haplotype analysis in prenatal diagnosis of monogenic diseases
- PMID: 36810160
- PMCID: PMC9947115
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202201761
Single-cell whole-genome sequencing, haplotype analysis in prenatal diagnosis of monogenic diseases
Abstract
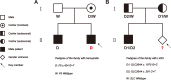
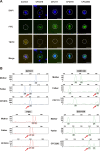
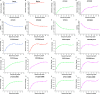
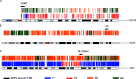
Monogenic inherited diseases are common causes of congenital disabilities, leading to severe economic and mental burdens on affected families. In our previous study, we demonstrated the validity of cell-based noninvasive prenatal testing (cbNIPT) in prenatal diagnosis by single-cell targeted sequencing. The present research further explored the feasibility of single-cell whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and haplotype analysis of various monogenic diseases with cbNIPT. Four families were recruited: one with inherited deafness, one with hemophilia, one with large vestibular aqueduct syndrome (LVAS), and one with no disease. Circulating trophoblast cells (cTBs) were obtained from maternal blood and analyzed by single-cell 15X WGS. Haplotype analysis showed that CFC178 (deafness family), CFC616 (hemophilia family), and CFC111 (LVAS family) inherited haplotypes from paternal and/or maternal pathogenic loci. Amniotic fluid or fetal villi samples from the deafness and hemophilia families confirmed these results. WGS performed better than targeted sequencing in genome coverage, allele dropout (ADO), and false-positive (FP) ratios. Our findings suggest that cbNIPT by WGS and haplotype analysis have great potential for use in prenatally diagnosing various monogenic diseases.
© 2023 Chang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Noninvasive prenatal testing for autosomal recessive conditions by maternal plasma sequencing in a case of congenital deafness.Genet Med. 2014 Dec;16(12):972-6. doi: 10.1038/gim.2014.51. Epub 2014 May 15. Genet Med. 2014. PMID: 24830326
-
A novel method for noninvasive diagnosis of monogenic diseases from circulating fetal cells.Prenat Diagn. 2021 Mar;41(4):400-408. doi: 10.1002/pd.5796. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Prenat Diagn. 2021. PMID: 32673403
-
Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of monogenic disorders based on direct haplotype phasing through targeted linked-read sequencing.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Oct 9;14(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-01091-x. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34627256 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Plasma DNA and RNA Sequencing for Prenatal Testing.Adv Clin Chem. 2016;74:63-102. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2015.12.004. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Adv Clin Chem. 2016. PMID: 27117661 Review.
-
Non-invasive prenatal testing for fetal chromosomal abnormalities by low-coverage whole-genome sequencing of maternal plasma DNA: review of 1982 consecutive cases in a single center.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Mar;43(3):254-64. doi: 10.1002/uog.13277. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24339153 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequencing of high-frequency mutated genes in breast cancer (BRCA) and associated-functions analysis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2025 Feb 15;18(2):46-62. doi: 10.62347/YODE5431. eCollection 2025. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40083350 Free PMC article.
-
Proband-independent haplotyping based on NGS-based long-read sequencing for detecting pathogenic variant carrier status in preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Mar 7;11:1329580. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1329580. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38516188 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-based Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (cbNIPT)-A Review on the Current Developments and Future Prospects.Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2023 Sep 1;66(3):636-648. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000798. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 37650673 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
