Standard patient training versus Vik-Asthme chatbot-guided training: 'AsthmaTrain' - a protocol for a randomised controlled trial for patients with asthma
- PMID: 36810168
- PMCID: PMC9945055
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-067039
Standard patient training versus Vik-Asthme chatbot-guided training: 'AsthmaTrain' - a protocol for a randomised controlled trial for patients with asthma
Abstract
Introduction: Therapeutic education for patients with asthma has been shown to reduce asthma morbidity. The high availability of smart phones provides the opportunity to furnish patient training via specifically designed chatbot applications. The goal of this protocol is to perform a first pilot comparison of traditional face to face versus chatbot-guided patient therapeutic education programmes for patients with asthma.
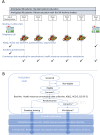
Methods and analysis: Eighty adult patients with a physician-confirmed diagnosis of asthma will be enrolled in a two-parallel-arm, randomised (1:1) controlled pilot trial. A single-Zelen consent procedure is deployed to first enrol all participants in the comparator arm, that is, the standard patient therapeutic education programme at the University Hospitals of Montpellier, France. This means of patient therapeutic education is based on reoccurring interviews and discussion with qualified nursing staff as per usual care. Following baseline data acquisition, randomisation will be performed. Those patients randomised to the comparator arm will not be informed of the second arm. Those patients randomised to the experimental arm will be proposed access to a specifically designed chatbot (Vik-Asthme) as the second tested means of patient training (refusals continue with standard training, though analysed as intention to treat). The primary outcome is change in the total Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire score at the end of follow-up (6 months). Secondary outcomes cover asthma control, spirometry, general health status, programme adherence and burden for medical staff, exacerbations and medical resource use (medications, consults, emergency visits, hospitalisation and intensive care).
Ethics and dissemination: This study ('AsthmaTrain' protocol version 4-20220330) has been approved by the Committee for the Protection of Persons Ile-de-France VII on 28 March 2022 (reference number 21.03617.000059). Enrolment began on 24 May 2022. Results will be published in international peer-reviewed journals.
Trial registration number: NCT05248126.
Keywords: Adult thoracic medicine; Asthma; MEDICAL EDUCATION & TRAINING.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: IV, DG, FC and FV report no competing interests. CMS reports grants and personal fees from Astra Zeneca, grants from GSK, outside the submitted work. NM reports personal fees from Astra Zeneca, grants from GSK, outside the submitted work. AB reports grants, personal fees, non-financial support and other from GSK, grants, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Astra Zeneca, grants, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Boeringher Ingelheim, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Novartis, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Chiesi Farma, non-financial support and other from Teva, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Sanofi Regeneron, grants, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Actelion/Jansen, other from United Therapeutics, other from Pulsar, personal fees, non-financial support and other from Roche, outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral and immunomodulatory interferon-beta in high-risk COVID-19 patients: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Sep 3;22(1):584. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05367-6. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34479601 Free PMC article.
-
Home Treatment of Older People with Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection (COVID-19): A structured Summary of a Study Protocol for a Multi-Arm Multi-Stage (MAMS) Randomized Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Tolerability of Several Experimental Treatments to Reduce the Risk of Hospitalisation or Death in outpatients aged 65 years or older (COVERAGE trial).Trials. 2020 Oct 13;21(1):846. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04619-1. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33050924 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of dexamethasone in patients with ARDS and COVID-19 - prospective, multi-centre, open-label, parallel-group, randomised controlled trial (REMED trial): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Mar 1;22(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05116-9. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33648568 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System blockade in patients admitted to hospital with confirmed coronavirus disease (COVID-19) infection (The McGill RAAS-COVID- 19): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Feb 5;22(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05080-4. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33546734 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing Medicine: Chatbots as Catalysts for Improved Diagnosis, Treatment, and Patient Support.Cureus. 2025 Mar 21;17(3):e80935. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80935. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40255778 Free PMC article. Review.
