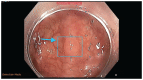
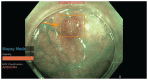
L’intelligence artificielle dans le dépistage du cancer colorectal
- PMID: 36810214
- PMCID: PMC9943565
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.220034-f
L’intelligence artificielle dans le dépistage du cancer colorectal
Conflict of interest statement
Intérêts concurrents: Michael Byrne est le chef de la direction, le fondateur et un actionnaire de Satisfai Health. Il est aussi le fondateur de la coentreprise AI4GI (qui a une entente de conception conjointe avec Olympus America dans le domaine de l’intelligence artificielle et des polypes colorectaux). Il a aussi déclaré une participation aux comités de la World Endoscopy Organization et de l’American Gastroenterological Association Tech Summit. Aucun autre intérêt concurrent n’a été déclaré.
Figures
References
-
- Leddin D, Lieberman DA, Tse F, et al. . Clinical practice guideline on screening for colorectal cancer in individuals with a family history of nonhereditary colorectal cancer or adenoma: the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Banff Consensus. Gastroenterology 2018;155:1325–1347.e3. - PubMed
-
- Aguilera-Chuchuca MJ, Sánchez-Luna SA, González Suárez B, et al. . The emerging role of artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal endoscopy: a review. Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;45:492–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
