Effects of Electrical Stimulation of the Cell: Wound Healing, Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Signal Transduction
- PMID: 36810478
- PMCID: PMC9944882
- DOI: 10.3390/medsci11010011
Effects of Electrical Stimulation of the Cell: Wound Healing, Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Signal Transduction
Abstract
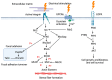
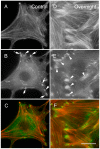
Electrical stimulation of the cell can have a number of different effects depending on the type of cell being stimulated. In general, electrical stimulation can cause the cell to become more active, increase its metabolism, and change its gene expression. For example, if the electrical stimulation is of low intensity and short duration, it may simply cause the cell to depolarize. However, if the electrical stimulation is of high intensity or long duration, it may cause the cell to become hyperpolarized. The electrical stimulation of cells is a process by which an electrical current is applied to cells in order to change their function or behavior. This process can be used to treat various medical conditions and has been shown to be effective in a number of studies. In this perspective, the effects of electrical stimulation on the cell are summarized.
Keywords: cell adhesion; cultured cells; cytoskeleton; electrical stimulation; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accelerated Skin Wound Healing by Electrical Stimulation.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Aug;10(16):e2100557. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202100557. Epub 2021 May 4. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 33945225 Review.
-
Accelerated Wound Healing on Skin by Electrical Stimulation with a Bioelectric Plaster.Adv Healthc Mater. 2017 Nov;6(22). doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700465. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. PMID: 28929631
-
A multi-scale feedback control system model for wound healing electrical activity: therapeutic device/protocol implications.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:3021-5. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2014.6944259. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25570627
-
Non-contact electrical stimulation as an effective means to promote wound healing.Bioelectrochemistry. 2022 Aug;146:108108. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2022.108108. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Bioelectrochemistry. 2022. PMID: 35366594
-
Effects of electrical stimulation on cell proliferation and apoptosis.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Mar;233(3):1860-1876. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25975. Epub 2017 Jun 6. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28452188 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduce electrical overload via threaded Chinese acupuncture in nerve electrical therapy.Bioact Mater. 2025 Jan 3;46:476-493. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.12.025. eCollection 2025 Apr. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 39850020 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Mesenchymal and Neural Stem Cells Response to Bipolar Microsecond Electric Pulses Stimulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 27;26(1):147. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010147. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796006 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical stimulation: a novel therapeutic strategy to heal biological wounds.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 11;14(44):32142-32173. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04258a. eCollection 2024 Oct 9. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39399261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conductive extracellular matrix derived/chitosan methacrylate/ graphene oxide-pegylated hybrid hydrogel for cell expansion.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 17;12:1398052. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1398052. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38952668 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Electrostimulation in a Standardized Setting.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 11;25(18):9808. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189808. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337300 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

