Rapidly Progressive Pauci-Immune Glomerulonephritis with Aberrant Fibrinoid Necrosis Associated with Atezolizumab, an Immune Check Point Inhibitor: A Case Report and Review of Literature
- PMID: 36810515
- PMCID: PMC9944432
- DOI: 10.3390/antib12010010
Rapidly Progressive Pauci-Immune Glomerulonephritis with Aberrant Fibrinoid Necrosis Associated with Atezolizumab, an Immune Check Point Inhibitor: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Abstract
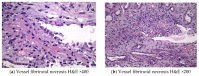
Stimulation of the antitumor activity of the immune system using immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has proven efficacy in the treatment of multiple types of cancer, inducing the speedily expanding approval of therapeutic indications for ICIs. The literature regarding the immune-related toxicities and nephrotoxicity of ICIs is limited. Herein, we present a patient with lung cancer treated with atezolizumab, an IgG1 monoclonal antibody aimed at the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), who presented with vasculitic skin rash and rapidly deteriorating renal function, new onset of significant glomerular hematuria and proteinuria. The renal biopsy revealed acute necrotizing pauci-immune vasculitis, with fibrinoid necrosis. The patient received a course of high-dose glucocorticoids with recovery of renal function and skin lesions. Further immunosuppressive therapy was withheld, due to active malignancy in the lung, while oncology consultation recommended the continuation of treatment with atezolizumab, as the patient had shown substantial response.
Keywords: acute kidney injury (AKI); checkpoint inhibitors; immune related adverse effect; immunotherapy; onconephrology; vasculitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal Vasculitis and Pauci-immune Glomerulonephritis Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.Am J Kidney Dis. 2019 Dec;74(6):853-856. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.04.016. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019. PMID: 31204194
-
Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with atezolizumab, an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (pd-l1) antibody therapy.Oncoimmunology. 2018 Mar 26;7(7):e1445952. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1445952. eCollection 2018. Oncoimmunology. 2018. PMID: 29900063 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence and Management of Pauci-Immune Glomerulonephritis and Vasculitis in Western Countries.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2016 Mar;1(4):224-34. doi: 10.1159/000442062. Epub 2015 Dec 5. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27536682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible atezolizumab-associated acute kidney injury and immune thrombocytopenia.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020 Oct;26(7):1791-1794. doi: 10.1177/1078155220913081. Epub 2020 Apr 1. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020. PMID: 32237958
-
The transition of renal histopathology after immunosuppressive therapy in a woman with renal limited ANCA-associated vasculitis: a case report and literature review.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016 May-Jun;34(3 Suppl 97):S115-20. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26841801 Review.
Cited by
-
The differentiation and intervention strategies for acute kidney injury after or induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors.Am J Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 15;15(4):1480-1493. doi: 10.62347/JECH8448. eCollection 2025. Am J Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40371140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors and renal toxicity.Heliyon. 2024 May 24;10(11):e31911. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31911. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38841501 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

