Signaling pathways in Parkinson's disease: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
- PMID: 36810524
- PMCID: PMC9944326
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01353-3
Signaling pathways in Parkinson's disease: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
Abstract
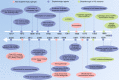
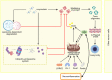
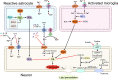
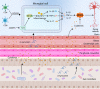
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease worldwide, and its treatment remains a big challenge. The pathogenesis of PD may be related to environmental and genetic factors, and exposure to toxins and gene mutations may be the beginning of brain lesions. The identified mechanisms of PD include α-synuclein aggregation, oxidative stress, ferroptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroinflammation, and gut dysbiosis. The interactions among these molecular mechanisms complicate the pathogenesis of PD and pose great challenges to drug development. At the same time, the diagnosis and detection of PD are also one of obstacles to the treatment of PD due to its long latency and complex mechanism. Most conventional therapeutic interventions for PD possess limited effects and have serious side effects, heightening the need to develop novel treatments for this disease. In this review, we systematically summarized the pathogenesis, especially the molecular mechanisms of PD, the classical research models, clinical diagnostic criteria, and the reported drug therapy strategies, as well as the newly reported drug candidates in clinical trials. We also shed light on the components derived from medicinal plants that are newly identified for their effects in PD treatment, with the expectation to provide the summary and outlook for developing the next generation of drugs and preparations for PD therapy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Charcot, J. M. Lecons sur, les maladies du système nerveux, Vol. 1 (Lecrosnier et Babé, 1886).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

