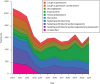
Over-the-counter cough and cold medicines: reported poisonings of children before and after the 2012 and 2020 labelling changes in Australia
- PMID: 36810714
- PMCID: PMC10953310
- DOI: 10.5694/mja2.51865
Over-the-counter cough and cold medicines: reported poisonings of children before and after the 2012 and 2020 labelling changes in Australia
Keywords: Common cold; Medical errors; Pharmacoepidemiology; Toxicology.
Conflict of interest statement
Rose Cairns has an untied educational grant from Reckitt to fund doctoral research concerning over‐the‐counter analgesics, unrelated to the content of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Preventing overdoses with over-the-counter medicines.Med J Aust. 2023 May 15;218(9):399-400. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51927. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Med J Aust. 2023. PMID: 37041656 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vassilev ZP, Kabadi S, Villa R. Safety and efficacy of over‐the‐counter cough and cold medicines for use in children. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2010; 9: 233‐242. - PubMed
-
- Dart RC, Paul IM, Bond GR, et al. Pediatric fatalities associated with over the counter (nonprescription) cough and cold medications. Ann Emerg Med 2009; 53: 411‐417. - PubMed
-
- Therapeutic Goods Administration . OTC cough and cold medicines for children: final outcomes of TGA review. 15 Aug 2012. Archived: https://web.archive.org/web/20140717013231/http://tga.gov.au/industry/ot... (viewed Feb 2023).
-
- Therapeutic Goods Administration . First‐generation oral sedating antihistamines: do not use in children [media release]. 13 July 2022. https://www.tga.gov.au/news/safety‐updates/first‐generation‐oral‐sedatin... (viewed Feb 2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical