In vivo osseointegration evaluation of implants coated with nanostructured hydroxyapatite in low density bone
- PMID: 36812287
- PMCID: PMC9946243
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282067
In vivo osseointegration evaluation of implants coated with nanostructured hydroxyapatite in low density bone
Abstract
Objective: This in vivo study, aimed to biomechanically, histomorphometrically and histologically evaluate an implant surface coated with nanostructured hydroxyapatite using the wet chemical process (biomimetic deposition of calcium phosphate coating) when compared to a dual acid-etching surface.
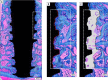
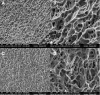
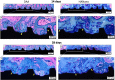
Material and methods: Ten sheep (2-4 years old) received 20 implants, 10 with nanostructured hydroxyapatite coating (HAnano), and 10 with dual acid-etching surface (DAA). The surfaces were characterized with scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy; insertion torque values and resonance frequency analysis were measured to evaluate the primary stability of the implants. Bone-implant contact (BIC) and bone area fraction occupancy (BAFo) were evaluated 14 and 28 days after implant installation.
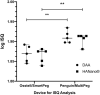
Results: The HAnano and DAA groups showed no significant difference in insertion torque and resonance frequency analysis. The BIC and BAFo values increased significantly (p<0.05) over the experimental periods in both groups. This event was also observed in BIC value of HAnano group. The HAnano surface showed superior results compared to DAA after 28 days (BAFo, p = 0.007; BIC, p = 0.01).
Conclusion: The results suggest that the HAnano surface favors bone formation when compared to the DAA surface after 28 days in low-density bone in sheep.
Copyright: © 2023 Almeida et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Influence of Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite Surface in the Early Stages of Osseointegration: A Multiparameter Animal Study in Low-Density Bone.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Nov 10;15:8803-8817. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S280957. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33204089 Free PMC article.
-
Histomorphometric and microtomographic evaluation of hydroxyapatite coated implants and L-PRF in over drilled bone sites in sheep.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 28;15(1):14761. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98126-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40295611 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo evaluation of cp Ti implants with modified surfaces by laser beam with and without hydroxyapatite chemical deposition and without and with thermal treatment: topographic characterization and histomorphometric analysis in rabbits.Clin Oral Investig. 2017 Mar;21(2):685-699. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1936-7. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Clin Oral Investig. 2017. PMID: 27530186
-
Increased osseointegration effect of bone morphogenetic protein 2 on dental implants: an in vivo study.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014 Jun;102(6):1921-7. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34862. Epub 2013 Jul 30. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014. PMID: 23853058
-
A systematic review on the effect of inorganic surface coatings in large animal models and meta-analysis on tricalcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite on periimplant bone formation.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022 Jan;110(1):157-175. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.34899. Epub 2021 Jul 16. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022. PMID: 34272804 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nano-Based Approaches in Surface Modifications of Dental Implants: A Literature Review.Molecules. 2024 Jun 27;29(13):3061. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133061. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Incorporation of Zinc into Hydroxyapatite and Its Influence on the Cellular Response to Biomaterials: A Systematic Review.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Jun 28;15(7):178. doi: 10.3390/jfb15070178. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39057300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Bacterial Growth on Titanium Surfaces Treated with Nanosized Hydroxyapatite.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Feb 16;16(2):66. doi: 10.3390/jfb16020066. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 39997600 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Various Implant Coatings on Bone Formation and Cell Adhesion.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025 Jun;17(Suppl 2):S1668-S1670. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_230_25. Epub 2025 Jun 18. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025. PMID: 40655667 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling Sodium Titanate Crystal Size to Improve Wettability and Early Osseointegration of Titanium Implants: Insights from an Animal Model.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Aug 1;16(8):283. doi: 10.3390/jfb16080283. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40863303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klein MO, Bijelic A, Ziebart T, Koch F, Kämmerer PW, Wieland M, et al. (2013) Submicron scale-structured hydrophilic titanium surfaces promote early osteogenic gene response for cell adhesion and cell differentiation. Clinical implant dentistry and related research 15: 166–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2011.00339.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wennerberg A & Albrektsson T (2009) Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: a systematic review. Clinical oral implants research 20 Suppl 4: 172–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

