Unmasking of the von Willebrand A-domain surface adhesin CglB at bacterial focal adhesions mediates myxobacterial gliding motility
- PMID: 36812310
- PMCID: PMC9946355
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abq0619
Unmasking of the von Willebrand A-domain surface adhesin CglB at bacterial focal adhesions mediates myxobacterial gliding motility
Abstract
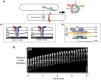
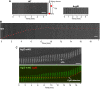
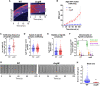
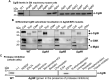
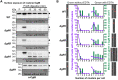
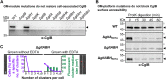
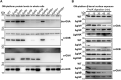
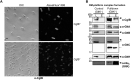
The predatory deltaproteobacterium Myxococcus xanthus uses a helically-trafficked motor at bacterial focal-adhesion (bFA) sites to power gliding motility. Using total internal reflection fluorescence and force microscopies, we identify the von Willebrand A domain-containing outer-membrane (OM) lipoprotein CglB as an essential substratum-coupling adhesin of the gliding transducer (Glt) machinery at bFAs. Biochemical and genetic analyses reveal that CglB localizes to the cell surface independently of the Glt apparatus; once there, it is recruited by the OM module of the gliding machinery, a heteroligomeric complex containing the integral OM β barrels GltA, GltB, and GltH, as well as the OM protein GltC and OM lipoprotein GltK. This Glt OM platform mediates the cell-surface accessibility and retention of CglB by the Glt apparatus. Together, these data suggest that the gliding complex promotes regulated surface exposure of CglB at bFAs, thus explaining the manner by which contractile forces exerted by inner-membrane motors are transduced across the cell envelope to the substratum.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Contact- and Protein Transfer-Dependent Stimulation of Assembly of the Gliding Motility Machinery in Myxococcus xanthus.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jul 1;11(7):e1005341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005341. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26132848 Free PMC article.
-
The mysterious nature of bacterial surface (gliding) motility: A focal adhesion-based mechanism in Myxococcus xanthus.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Oct;46:143-54. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.10.033. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26520023 Review.
-
The mechanism of force transmission at bacterial focal adhesion complexes.Nature. 2016 Nov 24;539(7630):530-535. doi: 10.1038/nature20121. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27749817 Free PMC article.
-
Structural model of a bacterial focal adhesion complex.Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 24;8(1):119. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07550-w. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39856386 Free PMC article.
-
Gliding motility in bacteria: insights from studies of Myxococcus xanthus.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999 Sep;63(3):621-41. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.63.3.621-641.1999. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10477310 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myxococcus xanthus predation: an updated overview.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 24;15:1339696. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1339696. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38328431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PilY1 regulates the dynamic architecture of the type IV pilus machine in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 30;15(1):9382. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53638-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39477930 Free PMC article.
-
Origin and Evolution of Bacterial Periplasmic Force Transducers.Mol Biol Evol. 2025 Jun 4;42(6):msaf138. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaf138. Mol Biol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40542537 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate stiffness modulates collective colony expansion of the social bacterium Myxococcus xanthus.APL Bioeng. 2025 Jan 17;9(1):016104. doi: 10.1063/5.0226619. eCollection 2025 Mar. APL Bioeng. 2025. PMID: 39845738 Free PMC article.
-
Milestones in the development of Myxococcus xanthus as a model multicellular bacterium.J Bacteriol. 2025 Jul 24;207(7):e0007125. doi: 10.1128/jb.00071-25. Epub 2025 Jun 17. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40525847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- S. T. Islam, I. Vergara Alvarez, F. Saïdi, A. Guiseppi, E. Vinogradov, G. Sharma, L. Espinosa, C. Morrone, G. Brasseur, J. F. Guillemot, A. Benarouche, J. L. Bridot, G. Ravicoularamin, A. Cagna, C. Gauthier, M. Singer, H. P. Fierobe, T. Mignot, E. M. F. Mauriello, Modulation of bacterial multicellularity via spatio-specific polysaccharide secretion. PLOS Biol. 18, e3000728 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- F. Saïdi, N. Y. Jolivet, D. J. Lemon, A. Nakamura, A. M. Belgrave, A. G. Garza, F. J. Veyrier, S. T. Islam, Bacterial glycocalyx integrity drives multicellular swarm biofilm dynamism. Mol. Microbiol. 116, 1151–1172 (2021). - PubMed
-
- F. Saïdi, U. Mahanta, A. Panda, A. A. Kezzo, N. Y. Jolivet, R. Bitazar, G. John, M. Martinez, A. Mellouk, C. Calmettes, Y. W. Chang, G. Sharma, S. T. Islam, Bacterial outer membrane polysaccharide export (OPX) proteins occupy three structural classes with selective β-barrel porin requirements for polymer secretion. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e01290-22 (2022). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

