A multiplexed, paired-pooled droplet digital PCR assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva
- PMID: 36813822
- PMCID: PMC9944410
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-29858-5
A multiplexed, paired-pooled droplet digital PCR assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: A multiplexed, paired-pooled droplet digital PCR assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 7;14(1):3155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52768-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38326320 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
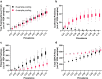
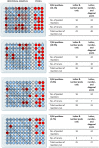
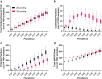
In response to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, we developed a multiplexed, paired-pool droplet digital PCR (MP4) screening assay. Key features of our assay are the use of minimally processed saliva, 8-sample paired pools, and reverse-transcription droplet digital PCR (RT-ddPCR) targeting the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid gene. The limit of detection was determined to be 2 and 12 copies per µl for individual and pooled samples, respectively. Using the MP4 assay, we routinely processed over 1,000 samples a day with a 24-h turnaround time and over the course of 17 months, screened over 250,000 saliva samples. Modeling studies showed that the efficiency of 8-sample pools was reduced with increased viral prevalence and that this could be mitigated by using 4-sample pools. We also present a strategy for, and modeling data supporting, the creation of a third paired pool as an additional strategy to employ under high viral prevalence.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

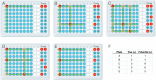
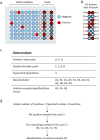
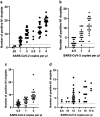

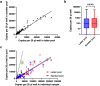

Similar articles
-
Sensitive SARS-CoV-2 detection, air travel Covid-19 testing, variant determination and fast direct PCR detection, using ddPCR and RT-qPCR methods.Acta Virol. 2023;67(1):3-12. doi: 10.4149/av_2023_101. Acta Virol. 2023. PMID: 36876506
-
Evaluation of diagnostic performance of SARS-CoV-2 infection using digital droplet polymerase chain reaction in individuals with or without COVID-19 symptoms.Clin Chim Acta. 2024 Feb 1;554:117759. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2023.117759. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Clin Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38184140
-
Sensitive detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2 by multiplex droplet digital RT-PCR.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021 Apr;40(4):807-813. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-04076-3. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33104899 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Different Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based Methods for Wastewater Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2: Exploratory Study.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Aug 19;10:e53175. doi: 10.2196/53175. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 39158943 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel, Reverse Transcription, Droplet Digital PCR Assay for the Combined, Sensitive Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 with Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus.J AOAC Int. 2022 Sep 6;105(5):1437-1446. doi: 10.1093/jaoacint/qsac039. J AOAC Int. 2022. PMID: 35377440
Cited by
-
Optimization and application of digital droplet PCR for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva specimen using commercially available kit.Biol Methods Protoc. 2024 Sep 23;9(1):bpae068. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpae068. eCollection 2024. Biol Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39355137 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 secondary attack rates and risks for transmission among agricultural workers and their households in Guatemala, 2022-2023.IJID Reg. 2025 May 27;16:100676. doi: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2025.100676. eCollection 2025 Sep. IJID Reg. 2025. PMID: 40606590 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluations of modes of pooling specimens for COVID-19 screened by quantitative PCR and droplet digital PCR.Sci Rep. 2024 May 13;14(1):10923. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61631-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38740976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CovidVaxView. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/imz-managers/coverage/covidvaxview/index.html.
-
- Thomas, K., Weiland, N. & LaFraniere, S. F.D.A. Advisory panel gives green light to pfizer vaccine. New York Times (2020).
-
- Booeshaghi, A. S., Tan, F., Renton, B., Berger, Z. & Pachter, L. Markedly heterogeneous COVID-19 testing plans among US colleges and universities. medRxiv 2020.08.09.20171223 (2020) doi:10.1101/2020.08.09.20171223.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

