Evaluating the indotecan-neutropenia relationship in patients with solid tumors by population pharmacokinetic modeling and sigmoidal Emax regressions
- PMID: 36813886
- PMCID: PMC10719825
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-023-04509-8
Evaluating the indotecan-neutropenia relationship in patients with solid tumors by population pharmacokinetic modeling and sigmoidal Emax regressions
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed at characterizing indotecan population pharmacokinetics and explore the indotecan-neutropenia relationship in patients with solid tumors.
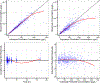
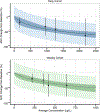
Methods: Population pharmacokinetics were assessed using nonlinear mixed-effects modeling of concentration data from two first-in-human phase 1 trials evaluating different dosing schedules of indotecan. Covariates were assessed in a stepwise manner. Final model qualification included bootstrap simulation, visual and quantitative predictive checks, and goodness-of-fit. A sigmoidal Emax model was developed to describe the relationship between average concentration and maximum percent neutrophil reduction. Simulations at fixed doses were conducted to determine the mean predicted decrease in neutrophil count for each schedule.
Results: 518 concentrations from 41 patients supported a three-compartment pharmacokinetic model. Body weight and body surface area accounted for inter-individual variability of central/peripheral distribution volume and intercompartmental clearance, respectively. Estimated typical population values were CL 2.75 L/h, Q3 46.0 L/h, and V3 37.9 L. The estimated value of Q2 for a typical patient (BSA = 1.96 m2) was 17.3 L/h, while V1 and V2 for a typical patient (WT = 80 kg) was 33.9 L and 132 L. The final sigmoidal Emax model estimated that half-maximal ANC reduction occurs at an average concentration of 1416 µg/L and 1041 µg/L for the daily and weekly regimens, respectively. Simulations of the weekly regimen demonstrated lower percent reduction in ANC compared to the daily regimen at equivalent cumulative fixed doses.
Conclusion: The final PK model adequately describes indotecan population pharmacokinetics. Fixed dosing may be justified based on covariate analysis and the weekly dosing regimen may have a reduced neutropenic effect.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01051635 NCT01794104.
Keywords: Indotecan; LMP400; PK-PD; Pharmacodynamics; Population pharmacokinetics.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
J.G. is a co-founder of Pumas AI, the company that developed the software, Pumas, which was used to develop this population PK model.
Figures

References
-
- Wang-Gillam A, Li C-P, Bodoky G, Dean A, Shan Y-S, Jameson G, Macarulla T, Lee K-H, Cunningham D, Blanc JF, Hubner RA, Chiu C-F, Schwartsmann G, Siveke JT, Braiteh F, Moyo V, Belanger B, Dhindsa N, Bayever E, Von Hoff DD, Chen L-T, Adoo C, Anderson T, Asselah J, Azambuja A, Bampton C, Barrios CH, Bekaii-Saab T, Bohuslav M, Chang D, Chen J-S, Chen Y-C, Choi HJ, Chung IJ, Chung V, Csoszi T, Cubillo A, DeMarco L, de Wit M, Dragovich T, Edenfield W, Fein LE, Franke F, Fuchs M, Gonzales-Cruz V, Gozza A, Fernando RH, Iaffaioli R, Jakesova J, Kahan Z, Karimi M, Kim JS, Korbenfeld E, Lang I, Lee F-C, Lee K-D, Lipton L, Ma WW, Mangel L, Mena R, Palmer D, Pant S, Park JO, Piacentini P, Pelzer U, Plazas JG, Prasad C, Rau K-M, Raoul J-L, Richards D, Ross P, Schlittler L, Smakal M, Stahalova V, Sternberg C, Seufferlein T, Tebbutt N, Vinholes JJ, Wadlow R, Wenczl M, Wong M (2016) Nanoliposomal irinotecan with fluorouracil and folinic acid in metastatic pancreatic cancer after previous gemcitabine-based therapy (NAPOLI-1): a global, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 387(10018):545–557. 10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00986-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee HM, Clark EP, Kuijer MB, Cushman M, Pommier Y, Philpot BD (2018) Characterization and structure–activity relationships of indenoisoquinoline-derived topoisomerase I inhibitors in unsilencing the dormant Ube3a gene associated with Angelman syndrome. Mol Autism 9:45. 10.1186/s13229-018-0228-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balana-Fouce R, Prada CF, Requena JM, Cushman M, Pommier Y, Alvarez-Velilla R, Escudero-Martinez JM, Calvo-Alvarez E, Perez-Pertejo Y, Reguera RM (2012) Indotecan (LMP400) and AM13–55: two novel indenoisoquinolines show potential for treating visceral leishmaniasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56(10):5264–5270. 10.1128/AAC.00499-12 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burton JH, Mazcko C, LeBlanc A, Covey JM, Ji J, Kinders RJ, Parchment RE, Khanna C, Paoloni M, Lana S, Weishaar K, London C, Kisseberth W, Krick E, Vail D, Childress M, Bryan JN, Barber L, Ehrhart EJ, Kent M, Fan T, Kow K, Northup N, Wilson-Robles H, Tomaszewski J, Holleran JL, Muzzio M, Eiseman J, Beumer JH, Doroshow JH, Pommier Y (2018) NCI comparative oncology program testing of non-camptothecin indenoisoquinoline topoisomerase I inhibitors in naturally occurring canine lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 24(23):5830–5840. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1498 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

